- Home
- Keboola Overview
- Getting Started Tutorial
-
Components
-
Data Source Connectors
- Communication
- Databases
- ERP
-
Marketing/Sales
- Adform DSP Reports
- Babelforce
- BigCommerce
- ChartMogul
- Criteo
- Customer IO
- Facebook Ads
- GoodData Reports
- Google Ads
- Google Ad Manager
- Google Analytics (UA, GA4)
- Google Campaign Manager 360
- Google Display & Video 360
- Google My Business
- Linkedin Pages
- Mailchimp
- Market Vision
- Microsoft Advertising (Bing Ads)
- Pinterest Ads
- Pipedrive
- Salesforce
- Shoptet
- Sklik
- TikTok Ads
- Zoho
- Social
- Storage
-
Other
- Airtable
- AWS Cost Usage Reports
- Azure Cost Management
- Ceps
- Dark Sky (Weather)
- DynamoDB Streams
- ECB Currency Rates
- Generic Extractor
- Geocoding Augmentation
- GitHub
- Google Search Console
- Okta
- HiBob
- Mapbox
- Papertrail
- Pingdom
- ServiceNow
- Stripe
- Telemetry Data
- Time Doctor 2
- Weather API
- What3words Augmentation
- YourPass
- Data Destination Connectors
- Applications
- Data Apps
- Development Branches
- IP Addresses
-
Data Source Connectors
-
Templates
- Advertising Platforms
- AI SMS Campaign
- Customer Relationship Management
- DataHub
- Data Quality
- eCommerce
- eCommerce KPI Dashboard
- Google Analytics 4
- Interactive Keboola Sheets
- Kai SQL Bot
- Mailchimp
- Media Cashflow
- Project Management
- Repository
- Snowflake Security Checkup
- Social Media Engagement
- Surveys
- UA and GA4 Comparison
- Data Catalog
- Storage
- Flows
- Orchestrations
-
Transformations
- Mappings
- Workspace
- Variables & Shared Code
- dbt Transformation
- Python Transformations
- R Transformations
- Snowflake Transformations
- BigQuery Transformations
- Redshift Transformations
- Synapse Transformations
- Exasol Transformations
- Teradata Transformations
- Oracle Transformations
- Code Patterns
- Legacy Sandbox
- Legacy Julia Transformations
- Legacy OpenRefine Transformations
- Legacy Python Transformations
- Legacy R Transformations
- Legacy Redshift Transformations
- Legacy Snowflake Transformations
- Transformation Migration
- Management
- AI Features
- Home
- Transformations
- Redshift Transformations
Redshift Transformation
AWS Redshift is based on PostgreSQL 8.0, where AWS added powerful scaling and made it available in the cloud. Transformations run on your own dedicated cluster in Keboola.
Example
To create a simple Redshift transformation, follow these steps:
- Create a table in Storage by uploading the sample CSV file.
- Create an input mapping from that table, setting its destination to
source. - Create an output mapping, setting its destination to a new table in your Storage.
- Copy & paste the below script into the transformation code.
- Save and run the transformation.
CREATE TABLE "result" AS SELECT * FROM "source";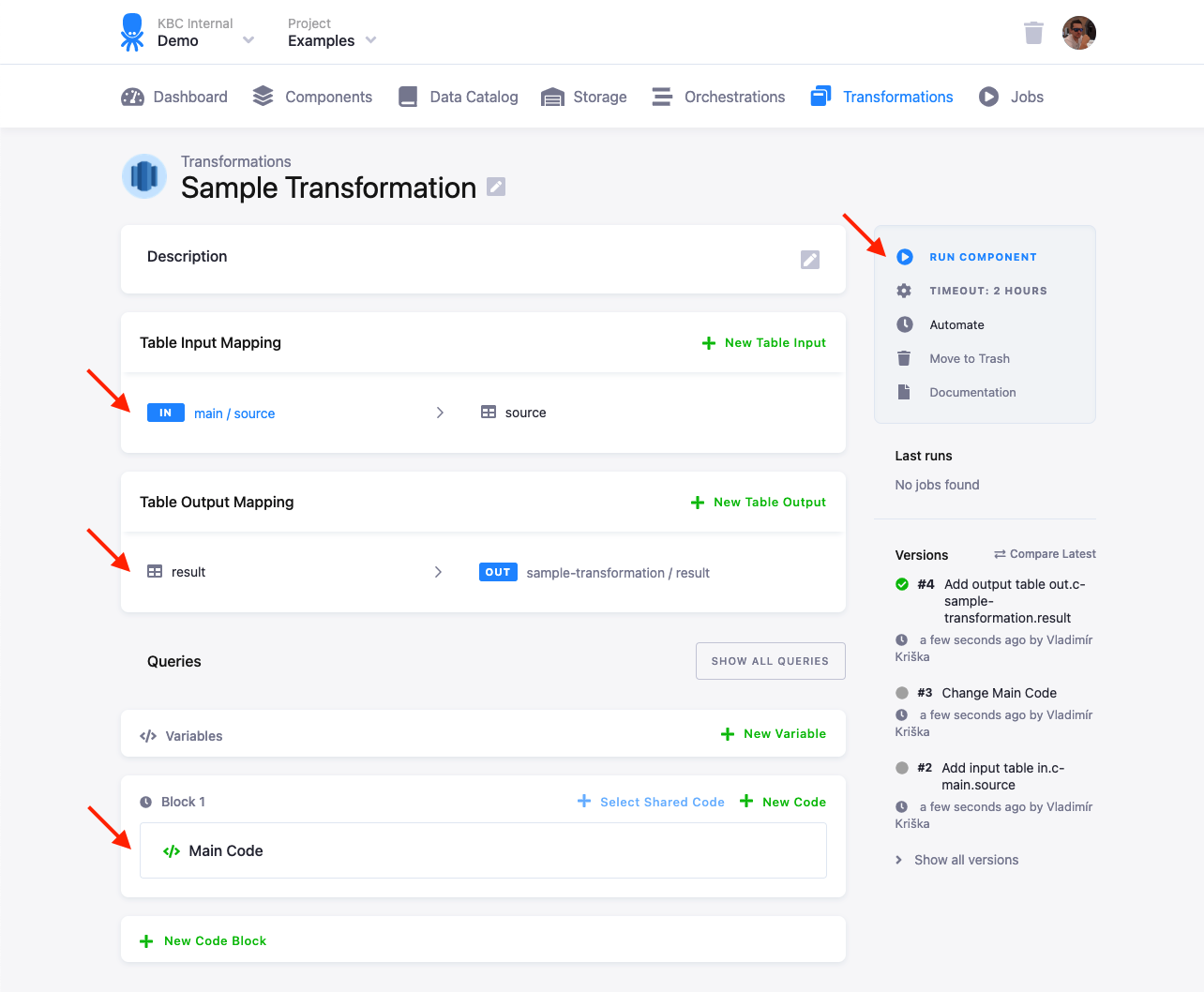
You can organize the script into blocks.
Limits
Redshift in Keboola does not support functions or stored procedures.
There are basic constraints set to keep your Redshift cluster healthy. By upgrading your Redshift cluster to a larger size, these limits can be increased.
- Redshift queries are limited to 3,600 seconds by default.
- All Redshift queries are performed on the cluster assigned to your project. By default, there is a limit of five concurrent queries. Additional queries will be queued.
- Queries containing comments longer than 8,192 characters will segfault.
Best Practices
Quoting: Use double quotes (") to encapsulate table and column names.
Case sensitivity: Redshift is case insensitive and stores all column and table names in lower case. However, Storage is case sensitive (be careful when migrating transformations to Redshift, letter case could cause problems in the output mapping).
© 2025 Keboola
