DataHub
The DataHub template provides a one-click setup of an end-to-end flow for populating Keboola metadata into a DataHub data catalog. This includes extracting data from the Telemetry and Metadata data source connectors before transforming the data to calculate table properties and lineage. You can choose whether or not to include schemas, properties, or tags from the DataHub data destination connector.
Prerequisites
Before you start, have a working instance of DataHub and get an API token.
Deploy DataHub
In order to get started, you must have a working (and secure!) instance of DataHub deployed somewhere. There are detailed deployment docs for the following platforms and technologies:
Deploying with Docker - DataHub
Deploying with Kubernetes - DataHub
Warning: Please ensure that you/the client have either removed or changed the credentials for the DataHub root user (default is datahub/datahub). Otherwise, you will get emails from “ethical security researchers” :-).
Generate API Token
For now, in order to generate the API token, you must make a graphQL call. This can be done by navigating to the dropdown menu in the upper righthand corner of DataHub. From there, open up GraphiQL and execute this mutation:
mutation {
createAccessToken(input: {type: PERSONAL,
actorUrn: "urn:li:corpuser:{{YOUR USERNAME}}}",
duration: {{LONG-LIVED (6months or 1 year)}},
name: "keboola-token"})
{
accessToken
metadata {
id
name
description
}
}
}
Make sure that you replace the username and duration above. Copy the token that is returned and store it securely until later, when it will be entered into Keboola.
The flow, in a nutshell
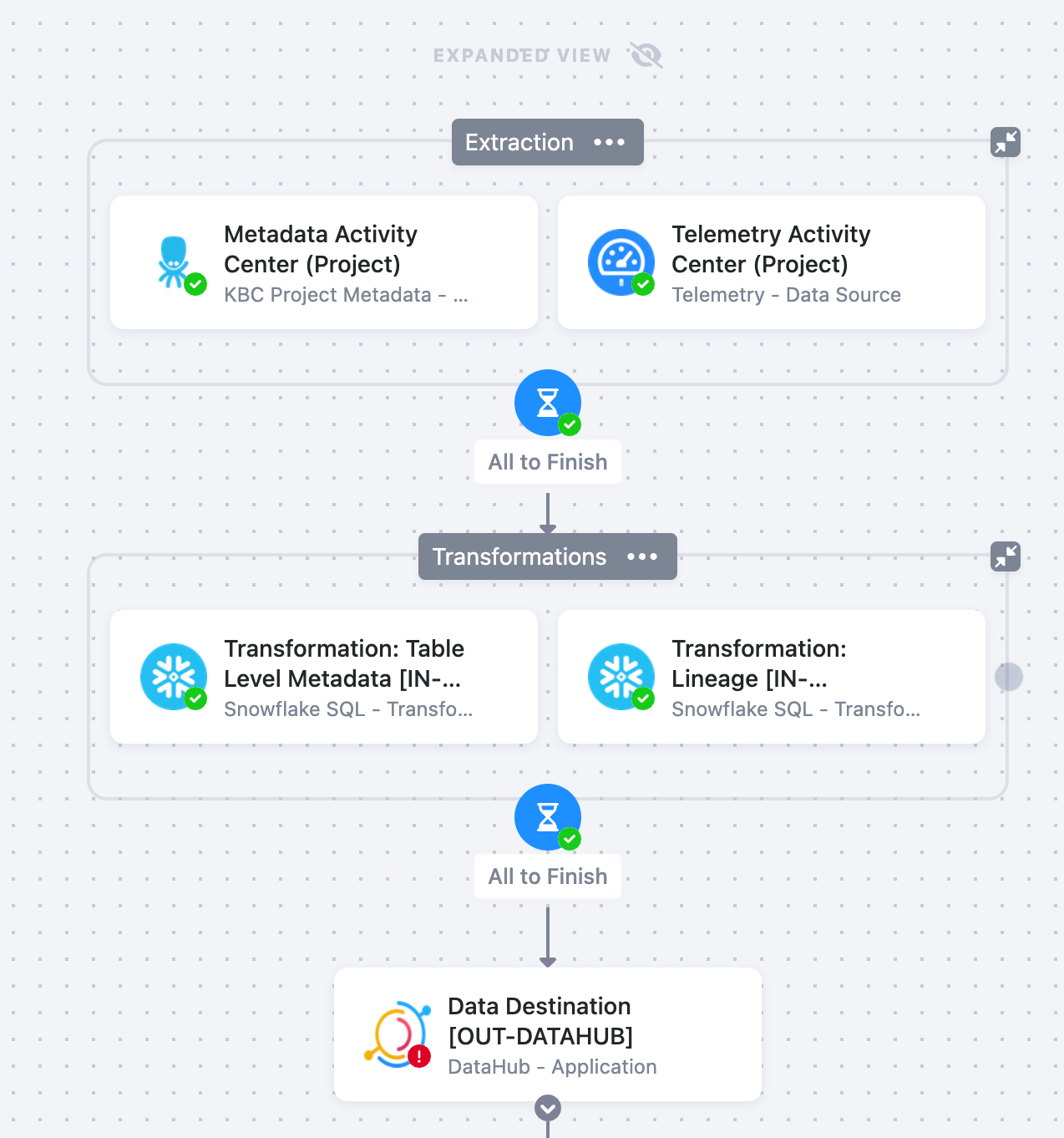
- First, the Metadata and Telemetry source connectors will collect the data from your project or organization.
- The Telemetry data source connector allows you to retrieve data pertaining to project or your entire organization. It helps you monitor the activities and usage of your Keboola projects. It also helps Keboola calculate your project consumption.
- The Metadata data source connector downloads information from Keboola’s APIs pertaining to various objects, users, etc. The metadata obtained by this source connector can be used in addition with the default telemetry data pertaining to Keboola projects to provide even more insights into the telemetry of your organization.
-
In the transformations, a single metadata table is created for transmitting information to DataHub. Lineage is also calculated by parsing component configurations.
-
In the final step, data will be pushed from storage to DataHub using the DataHub data destination connector. You will enter an API token and endpoint for your GMS (DataHub Metadata Service) server, as well as select the information you want to be included (e.g., properties, schemas, tags, etc.).
- Finally, you will run the entire flow (i.e., the sequence of all the prepared, above mentioned steps, in the correct order). The Metadata and Telemetry data source connectors, all data manipulations and analyses, and the DataHub data destination connector, will be processed.
Template/Component Variations
There is a bit of ambiguity here, so please take it with a grain of salt.
Transformation Details
There are currently two transformations that are a part of this template. The purpose of both is to bring together multiple pieces of metadata & telemetry for the purpose of emitting to DataHub.
Transformation 1: Table-Level Metadata
The transformation below does the following:
- First, it creates a temporary table called col_md_temp which contains table_id, region, project_id, column, and column level metadata.
- Next, it creates another temporary table called col_md which further partitions the data by table_id, column, and project_id.
- Following this, it creates another temporary table called table_md_temp which contains table_id, region, project_id, column, and column level metadata.
- Finally, it creates a table called tables_md_description which contains the table level metadata.
- Once these temporary tables are created, the SQL code uses a SELECT statement to query the data from the tables and combine it into a single table called “table-level-metadata”.
- The query selects the id, project_id, org_table_id, name, description, primary_key, rows_count, data_size_bytes, is_alias, bucket_id, bucket_name, last_import_date, last_change_date, source_table_id, project_name, table_columns, and table_level_md.
- The table_columns and table_level_md values are aggregated using the array_agg() function.
create or replace table "table-level-metadata" as
with col_md_temp as (
SELECT
"table_id",
"region",
"project_id",
"column",
object_agg(
(
concat("provider", '_', "key")
),
"value" :: variant
) over(
partition by(
"table_id", "column", "project_id"
)
) as "column_level_md"
FROM
"tables-columns-metadata"
),
col_md as(
select
"table_id",
"region",
"project_id",
"column",
"column_level_md"
from
col_md_temp
group by
1,
2,
3,
4,
5
),
table_md_temp as(
select
tc."table_id",
tc."region",
tc."project_id",
tc."column",
cmd."column_level_md"
from
"tables-columns" tc
left join col_md cmd on tc."table_id" = cmd."table_id"
and tc."column" = cmd."column"
and tc."project_id" = cmd."project_id"
),
tables_md_description as (
select * from "tables-metadata"
where "key" = 'KBC.description'
)
SELECT
t."id",
t."project_id",
concat(t."project_id", '.', t."id") as org_table_id,
t."name",
tables_md_description."value" as "description",
t."primary_key",
t."rows_count",
t."data_size_bytes",
t."is_alias",
t."bucket_id",
t."bucket_name",
t."last_import_date",
t."last_change_date",
t."source_table_id",
p."kbc_project" as "project_name",
array_agg(tmd."column")::varchar as "table_columns",
array_agg(object_construct(tmd."column", tmd."column_level_md"))::varchar as "table_level_md"
FROM
"tables" t
LEFT JOIN table_md_temp tmd on t."id" = tmd."table_id" and t."project_id" = tmd."project_id"
LEFT JOIN tables_md_description on t."id" = tables_md_description."table_id"
LEFT JOIN "kbc_project" p on t."project_id" = p."kbc_project_id_num"
group by
1,
2,
3,
4,
5,
6,
7,
8,
9,
10,
11,
12,
13,
14,
15
Transformation 2: Lineage
This transformation does the following:
- First, it creates a table called “configuration_json” that contains the configuration data parsed from the JSON configuration files.
- Next, it creates a table called “rows_json” that contains the row data parsed from the JSON configuration files.
- Then it creates a table called “configurations_parsed” that combines the configuration and row data into one table.
- Finally, it creates a table called “storage_inputs_and_outputs” that contains the storage input and output data parsed from the configurations_parsed table.
/* ===== BLOCK: Block 1 ===== */
/* ===== CODE: Configuration JSON ===== */
create or replace table "configuration_json" as
select
"id",
"region",
"project_id",
"name",
"created",
"creator_token_id",
"creator_token_description",
"component_id",
"component_name",
"component_type",
"version",
"is_deleted",
"current_version_created",
"current_version_creator_token_id",
"current_version_creator_token_description",
"current_version_change_description",
"description",
"configuration",
"rows",
configs.seq as config_seq,
configs.key as config_key,
configs.path as config_path,
configs.index as config_index,
configs.value as config_value,
configs.this as config_this
from
"configurations" c,
lateral flatten(
parse_json(c."configuration"),
recursive => true,
outer => true
) configs;
/* ===== CODE: Configuration Rows JSON ===== */
create or replace table "rows_json" as
select
"id",
"region",
"project_id",
"name",
"created",
"creator_token_id",
"creator_token_description",
"component_id",
"component_name",
"component_type",
"version",
"is_deleted",
"current_version_created",
"current_version_creator_token_id",
"current_version_creator_token_description",
"current_version_change_description",
"description",
"configuration",
"rows",
"rows".seq as config_seq,
"rows".key as config_key,
"rows".path as config_path,
"rows".index as config_index,
"rows".value as config_value,
"rows".this as config_this
from
"configurations" c,
lateral flatten(
parse_json(c."rows"),
recursive => true,
outer => true
) "rows";
/* ===== CODE: Configurations Parsed ===== */
create or replace table "configurations_parsed" as
select c.*,
p."kbc_project" as "project_name"
from (
select *
from "rows_json" c
union all
select *
from "configuration_json" c
) as c
left join "kbc_project" p ON p."kbc_project_id_num" = c."project_id";
/* ===== BLOCK: Block 2 ===== */
/* ===== CODE: Storage Inputs & Outputs ===== */
create or replace table "storage_inputs_and_outputs" as
with storage_inputs_sources as (
select
"id",
"region",
"project_id",
"project_name",
"name",
"component_id",
"component_name",
"component_type",
config_path,
CASE WHEN config_path LIKE 'storage.input.tables[%].source'
and config_path not like '%column%' THEN array_agg(config_value) END AS storage_inputs_sources
from
"configurations_parsed"
--where path LIKE 'storage.input.tables[%].source' and path not like '%column%'--or path = 'storage.output.tables'
group by
1,
2,
3,
4,
5,
6,
7,
8,
9
),
storage_inputs_destinations as (
select
"id",
"region",
"project_id",
"project_name",
"name",
"component_id",
"component_name",
"component_type",
config_path,
CASE WHEN config_path LIKE 'storage.input.tables[%].destination'
and config_path not like '%column%' THEN array_agg(config_value) END AS storage_inputs_destinations
from
"configurations_parsed"
group by
1,
2,
3,
4,
5,
6,
7,
8,
9
),
storage_outputs_sources as (
select
"id",
"region",
"project_id",
"project_name",
"name",
"component_id",
"component_name",
"component_type",
config_path,
CASE WHEN config_path LIKE 'storage.output.tables[%].source'
and config_path not like '%column%' THEN array_agg(config_value) END AS storage_outputs_sources
from
"configurations_parsed"
--where path LIKE 'storage.input.tables[%].source' and path not like '%column%'--or path = 'storage.output.tables'
group by
1,
2,
3,
4,
5,
6,
7,
8,
9
),
storage_outputs_destinations as (
select
"id",
"region",
"project_id",
"project_name",
"name",
"component_id",
"component_name",
"component_type",
config_path,
CASE WHEN config_path LIKE 'storage.output.tables[%].destination'
and config_path not like '%column%' THEN array_agg(config_value) END AS storage_outputs_destinations
from
"configurations_parsed" --where path LIKE 'storage.input.tables[%].source' and path not like '%column%'--or path = 'storage.output.tables'
group by
1,
2,
3,
4,
5,
6,
7,
8,
9
)
select
"id",
"region",
"project_id",
"project_name",
"name",
"component_id",
"component_name",
"component_type",
ARRAY_TO_STRING( storage_inputs_sources , ',' ) as storage_inputs_sources,
ARRAY_TO_STRING(storage_inputs_destinations, ',') as storage_inputs_destinations,
ARRAY_TO_STRING(storage_outputs_sources, ',') as storage_outputs_sources,
ARRAY_TO_STRING(storage_outputs_destinations, ',') as storage_outputs_destinations
from
storage_inputs_sources
left join storage_inputs_destinations using(
"id", "region", "project_id",
"project_name", "name",
"component_id", "component_name",
"component_type", config_path
)
left join storage_outputs_sources using(
"id", "region", "project_id",
"project_name","name",
"component_id", "component_name",
"component_type", config_path
)
left join storage_outputs_destinations using(
"id", "region", "project_id",
"project_name","name",
"component_id", "component_name",
"component_type", config_path
)
where STORAGE_INPUTS_SOURCES is not null or STORAGE_OUTPUTS_DESTINATIONS is not null;
