External Datasets
If you operate Keboola in Bring Your Own Database (BYODB) mode using your own data warehouse, the data in the warehouse won’t automatically be visible or accessible within Keboola. To address this, we offer the External Datasets feature.
The implementation of External Datasets requires the BYODB to be enabled first. Unless specified otherwise, this description refers to the implementation of Snowflake and BigQuery.
What Is an External Dataset?
Storage in Keboola is organized into buckets. An external dataset is a special type of bucket wherein Keboola does not manage its content. It can be located anywhere in the storage backend used by your Keboola project (Snowflake or BigQuery) and is a virtual bucket connected to a Snowflake schema or BigQuery dataset, respectively.
All table-like objects (such as tables, views, and external tables) inside the schema (in Snowflake) or dataset (in BigQuery) are mapped to tables in the bucket. Access to the bucket is read-only; you cannot write to the bucket from Keboola. A single schema can be registered simultaneously with multiple projects in Keboola.
Creating an External Dataset
An external dataset can be registered in the Storage of a project. Navigate to Storage > Register External Dataset. The dialog will differ based on the backend you are using.
Snowflake
Fill in the name of the new bucket, database name, and schema name. Click Next Step. Keboola will then generate a code that you can use to grant Keboola correct access to the schema in your Snowflake. Once access has been granted, click Register Dataset to start using it.
Note: This set of permissions grants the Keboola service account read-only access to the data.
Sharing data via Snowflake is currently not supported. Attempting to grant permissions will result in an error.
BigQuery
Fill in the name of the new dataset and dataset name. Click Next Step. Keboola will generate a code that you can use to grant Keboola correct access to the dataset in BigQuery. Once access has been grated, click Register Dataset to start using it.
Note: By adding the Keboola service account as a subscriber, you enable read-only access to the data.
BigLake Tables
Keboola generaly does not support external tables, except for BigLake tables. Please ensure that any table you are using is of this type. External tables of other types will not work in transformations and workspaces due to permission issues.
Please ensure that you can perform a SELECT * FROM <table> LIMIT 1 query on your created BigLake table. Keboola checks this during the registration process.
If the SELECT fails, the table will be skipped.
The only exceptions are tables configured with require_hive_partition_filter=true. Such configurations of BigLake tables are supported by Keboola, but
SELECT operations (like Data Preview) will fail. This is expected behavior. You can still use these tables in your workspaces and transformations, but
appropriate WHERE conditions are necessary.
Using an External Dataset
When you register an external dataset, we analyze the metadata of the objects in it and register all tables and views as tables in the Keboola Storage bucket. If you later add additional tables or views, you must manually refresh the Storage bucket using the Refresh action in the bucket detail to make them visible in Keboola.
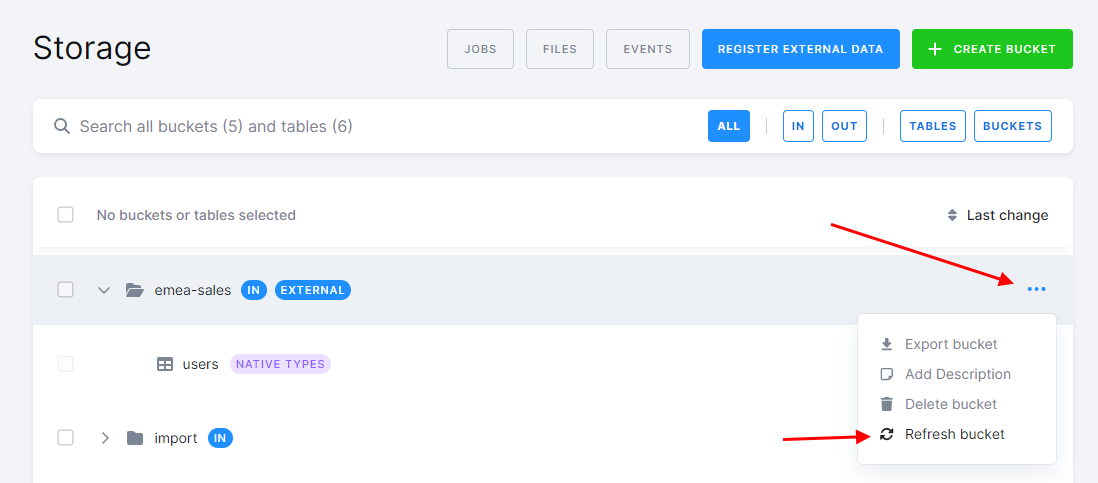
External datasets cannot be used in an input mapping They are accessible via the read-only input mapping. Keep in mind that external buckets cannot be used in an output mapping as they are not writable.
External Dataset in a Snowflake SQL Transformation
External datasets cannot be used in an input mapping as they are not copied into your transformation workspace. You need to reference them in your transformation using a fully qualified name.
In the following example, it is assumed that you’ve created an external dataset called users-reporting that references the sales_emea schema in the database
REPORTING. The schema contains a table called users. Now you want to create a new table MQL_USERS that contains only users sourced from
marketing-qualified leads. You can do that using the following SQL:
CREATE TABLE "MQL_USERS" AS SELECT *
FROM "REPORTING"."sales_emea"."users"
WHERE "source" = 'mql';
Note: The query uses the fully qualified name of the table in the FROM clause.
External Dataset in a BigQuery SQL Transformation
For BigQuery, an external dataset is mapped to an actual dataset, users_reporting (the name you filled in the dialog), in your project—in this case, project sapi-9752. You can reference the contents of the dataset in your SQL transformation using a fully qualified name:
CREATE TABLE `MQL_USERS` AS SELECT *
FROM `users_reporting`.`users`
WHERE `source` = "mql";
Note: The dataset name is the name of the bucket you provided in the dialog (users-reporting), not that of the original dataset created in BigQuery
(sales_emea). However, there are no technical limitations; they can have the same name.
Removing an External Dataset
Removing an external dataset is as simple as removing any other Storage bucket. Simply delete it in the UI or via API. The Storage bucket will be removed from the project, but the schema in the database will remain untouched. Any rights that you have granted to Keboola during the registration will be revoked.
If you wish to remove the schema, you must do so manually in your warehouse.
Usage Recommendations
- Use external datasets to work with data in your warehouse that has been produced by third-party tools outside Keboola.
- Use external datasets to access data in table-like structures that are not directly supported by Keboola (e.g., views and external tables).
- Using external datasets to load data from services with existing components into Keboola is discouraged. Consider the following limitations of such an approach:
- You would have to orchestrate, maintain, and monitor the external pipeline, which Keboola normally does for you.
- Manipulation of the data will not be tracked in the Keboola audit trail.
- Event-driven triggering is not supported for external datasets, so you must manually synchronize the external and Keboola pipelines based on time.
- While there are legitimate uses of external tools, keep in mind that by having data pipelines outside Keboola, you lose the main benefit of Keboola—the ability to orchestrate, maintain, monitor, and audit the pipelines in one place.
Limitations
- Table names can’t be longer than 92 characters and can contain only alphanumeric characters, dashes, and underscores. Tables that do not meet these requirements will be ignored.
- Table names are not case-sensitive. You cannot create two tables with the same name that differ only in letter case.
- Creating snapshots from tables in external buckets is not supported.
- Sharing with other projects is not supported at the moment.
- A read-only input mapping with an external dataset has a limitation. If you delete and recreate a registered table in the source schema, our read-only input mapping will lose access to this table. This occurs because we aim to limit clients from having excessive permissions, such as OWNERSHIP, on their external schemas. However, manually refreshing the bucket addressess this issue.
To permanently resolve this issue, you can manually grant the read-only input mapping role future access to your tables as illustrated below:
GRANT SELECT ON FUTURE TABLES IN SCHEMA "REPORTING"."sales_schema" TO ROLE KEBOOLA_8_RO
Ensure the role name follows the pattern in the picture and is suffixed with _RO.
