Tables
The Table Storage for your project is available under the Tables tab in the Storage section. All data tables are organized into buckets that can also be used to share tables between projects.
The actual data tables and the buckets are created primarily by Keboola components (data source connectors, transformations, and applications), or they are imported from CSV files. If you want to import data into an already existing table, the imported table must contain all the columns of the existing table, even if the existing table is empty. If any columns are missing, you will receive an error message similar to the following:
Some columns are missing in the CSV file. Missing columns: lat,long. Expected columns: lat,long.
Please check if the expected "," delimiter is used in the CSV file.
The imported file may also contain additional columns not present in the existing table. In that case, the columns from the imported table will be added to the existing table.
Table and column names can contain only alphanumeric characters. Dash and
underscores are allowed. Column names must not start or end with dash - or underscore
character _.
When you select a table from any bucket in Storage, detailed information about the table will be displayed at the top of the screen. This is what we refer to as the table detail throughout our documentation.
Aliases
Apart from actual tables, it is also possible to create aliases. They behave similarly to database views.
An alias does not contain any actual data; it is simply a link to some already existing data. Therefore, an alias cannot be written to, and its size does not count toward your project quota.
To create an alias table, go to the table detail, click the three dots on the right side of the screen, and select the ‘Create alias table’ option.
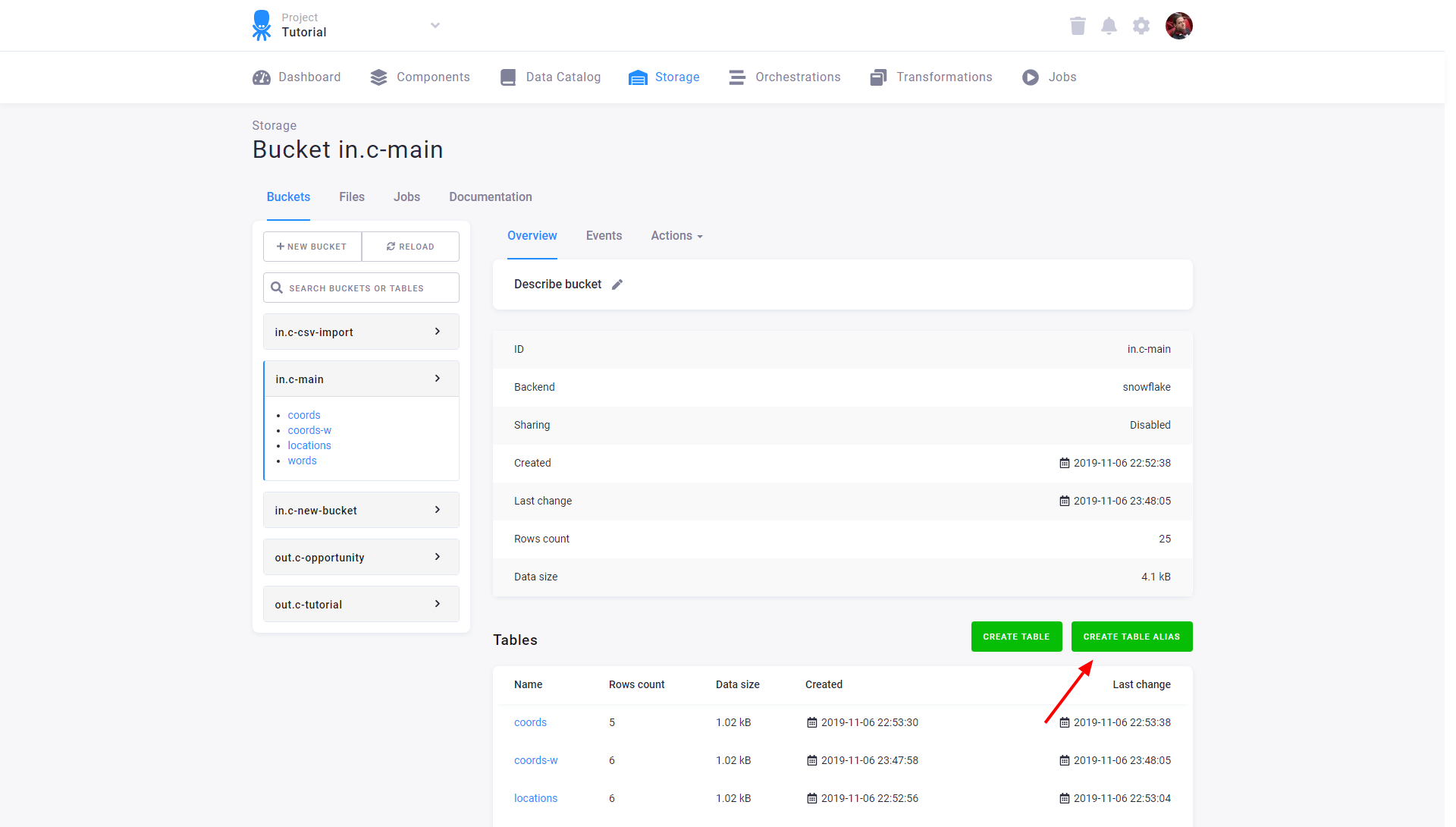
An alias table can be filtered by a simple condition.
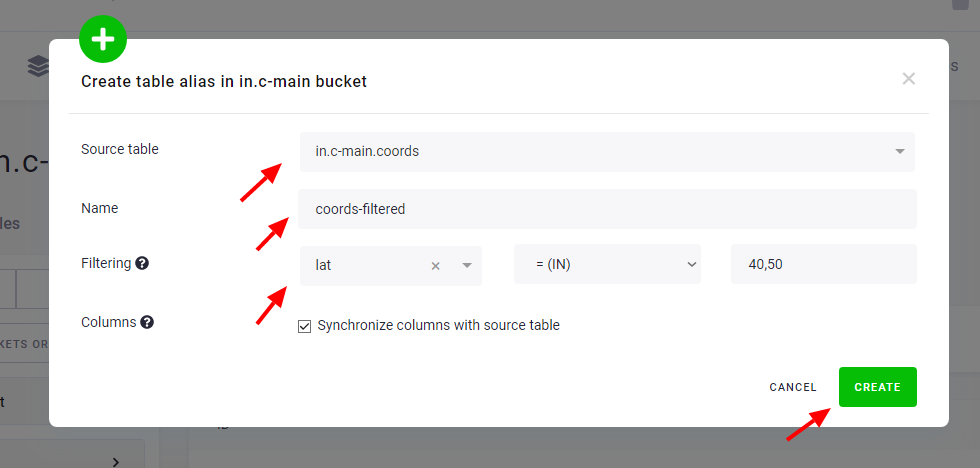
The table detail of an alias table contains additional information, including a reference to the source table from which it was created and any filters applied to the alias. Note that you can adjust the alias filters even after the alias table has been created.
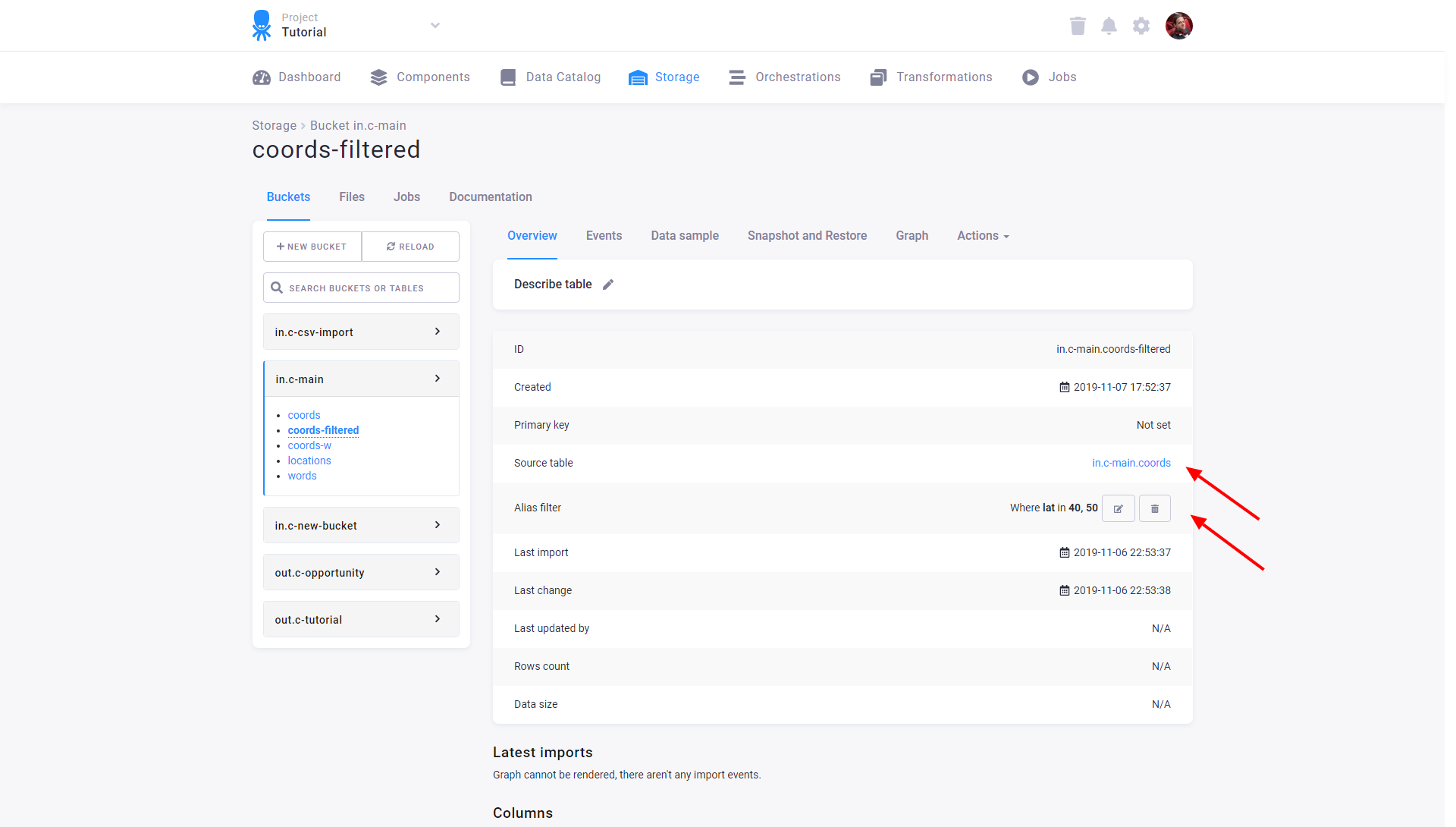
When attempting to delete a table with alias tables elsewhere in Storage, you will be prompted with a notification as part of the deletion process. The notification will detail the aliases (including links) connected to the table. You must confirm that you understand the aliases will be deleted as well before proceeding.
By default, alias columns are automatically synchronized with the source table. Columns added to the source table will be added to the alias automatically. You can prevent this by disabling Synchronize columns with source table.
Aliases with automatically synchronized columns and without a filter can be chained.
Metadata
Each Table Storage object (bucket, table, column) has an associated key-value store. This can be used to store arbitrary metadata (information about the data itself). Apart from arbitrary user-defined metadata, there is also some information stored automatically. For example, each bucket and table has information about which configuration of which component created them. One important use case of metadata is Column Data Types.
Primary Keys
Each table may have a primary key defined on one or more columns. A primary key represents an identifier of each row in the table. Each primary key can be defined manually on a table or as part of output mapping of transformations and applications. The settings on both places must match, otherwise you will receive an error:
Output mapping does not match destination table: primary key '' does not match 'Id' in 'out.c-tutorial.opportunity_denorm' (check transformations Denormalize opportunities (id opportunity.denormalize-opportunities)).
This means that you cannot change the primary key of a table arbitrarily. Also note that you cannot set the primary key on a column which contains duplicates — you will receive the following error:
Cannot create new primary key, duplicate values in primary key columns
If you want to manually set a primary key on a table, you can do so in Storage:
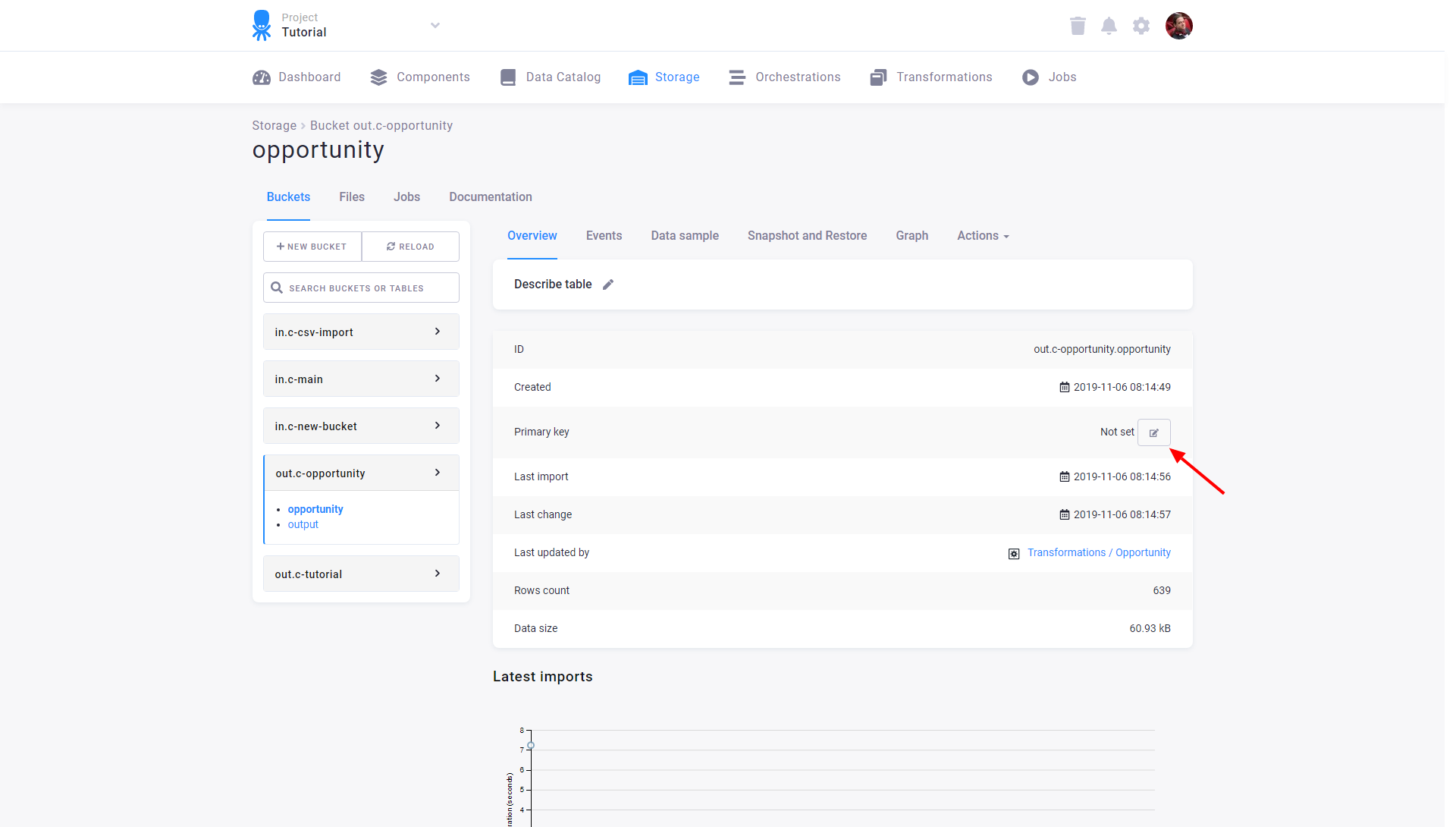
Then select the columns you wish to add to the primary key:
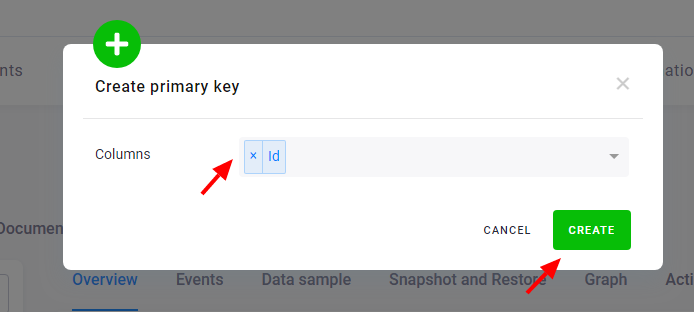
To remove an existing primary key, click the bin icon:
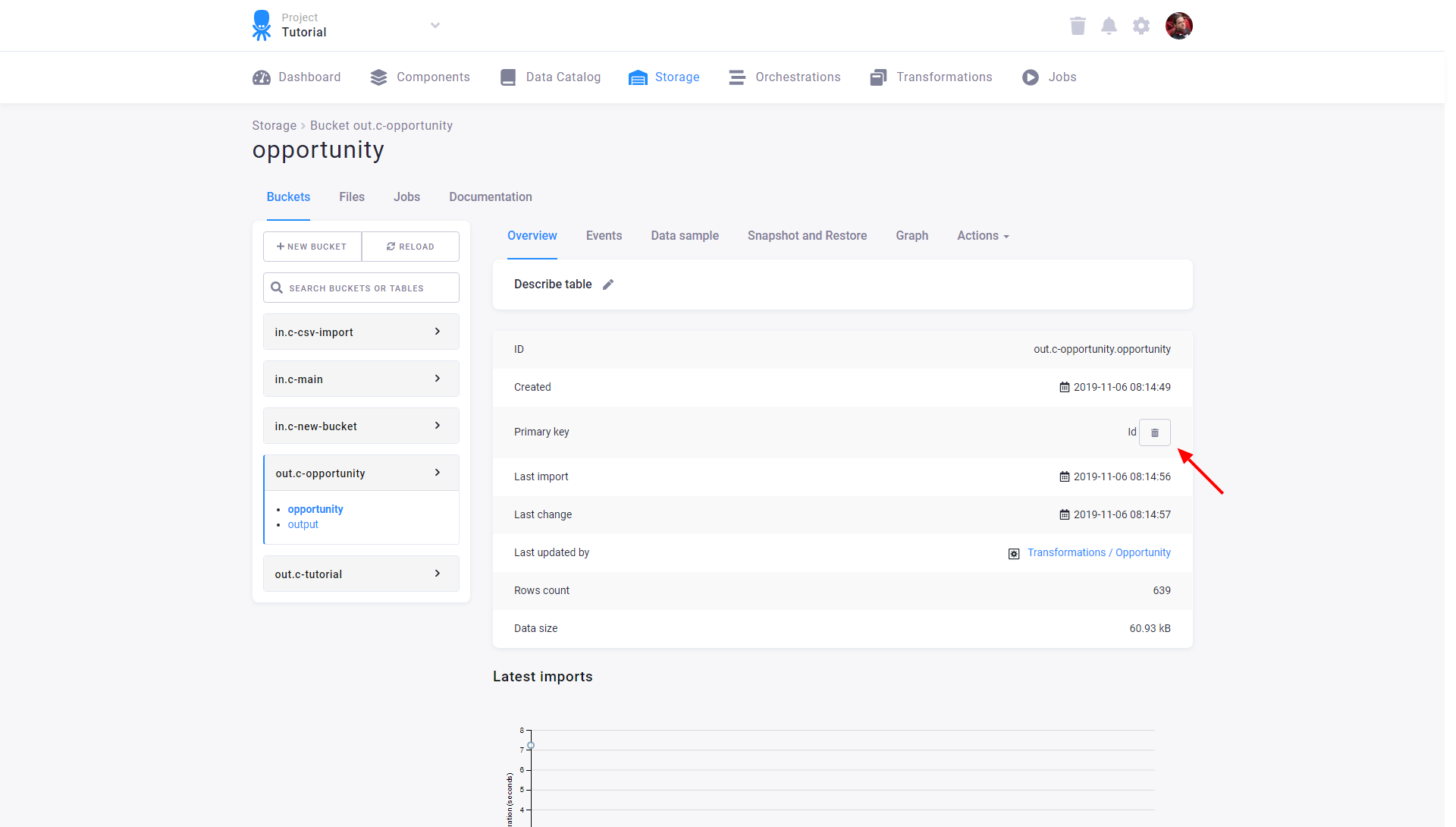
Note: Be aware that creating or removing the primary key can take some time on large tables.
Primary Key Deduplication
When a primary key is defined on a column, the value of that column is guaranteed to be unique in that table.
As data is loaded into the table, only one of the rows with duplicate values is preserved.
All the other duplicates are ignored.
Let’s say you have a table with two columns: name and money. The primary key is defined
on the column name.
| name | money |
|---|---|
| John | $150 |
| John | $340 |
| Darla | $600 |
| Annie | $500 |
| John | $340000 |
| Darla | $600000 |
Their uniqueness is checked and the data are de-duplicated. The result table looks like this:
| name | money |
|---|---|
| Darla | $600 |
| John | $340000 |
| Annie | $500 |
The order of rows in the imported file is not important and is not kept. That means that from each of
the duplicate rows a randomly selected one is kept and all others are discarded.
In our example, the rows John,$150, John,$340 and Darla,$60000 were discarded.
With a primary key defined on multiple columns, the combination of their values is unique.
Let’s say you have a table with three columns: name, age and money. The primary key is defined
on two of them: name and age.
When you load the following data into your table:
| name | age | money |
|---|---|---|
| John | 15 | $150 |
| John | 34 | $340 |
| Darla | 60 | $600 |
| Annie | 30 | $500 |
| John | 34 | $340000 |
| Darla | 60 | $600000 |
their uniqueness is checked and the data are de-duplicated. The result table looks like this:
| name | age | money |
|---|---|---|
| John | 15 | $150 |
| Darla | 60 | $600 |
| John | 34 | $340000 |
| Annie | 30 | $500 |
Again, the order of rows in the imported file is not important and is not kept.
In our example, the rows John,34,$340 and Darla,60,$600000 were discarded.
Incremental Loading
When a primary key is defined on a column, it is also possible to take advantage of incremental loads.
If you load data into a table incrementally, new rows will be added and existing rows will be updated
unless they are completely identical to the existing rows. No rows will be deleted.
If you have a table with a primary key defined on the column name:
| name | money |
|---|---|
| John | $150 |
| Peter | $340 |
| Darla | $600 |
and you import the following data to the table:
| name | money |
|---|---|
| Annie | $500000 |
| Peter | $340000 |
| Darla | $600000 |
the result table will contain:
| name | money |
|---|---|
| John | $150 |
| Darla | $600000 |
| Peter | $340000 |
| Annie | $500000 |
When importing data into a table with a primary key, the uniqueness is checked.
The record Peter,$340000 will overwrite the row Peter,$340, because it has the same primary key value.
The above applies only when incremental load is used.
When an incremental load is not used, the contents of the target table are cleared before the load. When a primary key is not defined and an incremental load is used, it simply appends the data to the table and does not update anything.
Difference between tables with native datatypes and string tables
There is significant change when loading incrementally into table with native datatypes on. If a table does not have native datatypes eanbled during incremental loading, the _timestamp column is updated based on the primary key only when a value in the row changes. In tables with native datatypes, the _timestamp column is updated every time when duplicate primary keys are imported. This behavior has an impact on incremental processing. When rows with duplicate primary keys are imported into tables with native types, they are treated as new rows.
Example:
- Keboola Storage table newly created at Tue Nov 22 2022 15:37:19 GMT+0000 (1669131439)
| ID | NAME | SKU | VALUE | DATE | _timestamp |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | John | CD-CZ-01 | 9247 | 2005-12-11 | 1669131439 |
| 2 | Jack | CE-CA-22 | 3544 | 2012-10-14 | 1669131439 |
| 3 | Jim | ED-BT-13 | 5262 | 2001-04-20 | 1669131439 |
| 4 | Jil | BA-AB-11 | 5278 | 2014-12-14 | 1669131439 |
- Incremental import A1 at Wed Nov 23 2022 16:41:20 GMT+0000 (1669221680)
| ID | NAME | SKU | VALUE | DATE | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| new row => | 5 | Andy | AB-CF-48 | 7081 | 2003-07-05 |
| new row => | 6 | Beth | HH-FR-14 | 7541 | 2002-04-01 |
- Result of incremental import A1
| ID | NAME | SKU | VALUE | DATE | _timestamp | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | John | CD-CZ-01 | 9247 | 2005-12-11 | 1669131439 | |
| 2 | Jack | CE-CA-22 | 3544 | 2012-10-14 | 1669131439 | |
| 3 | Jim | ED-BT-13 | 5262 | 2001-04-20 | 1669131439 | |
| 4 | Jil | BA-AB-11 | 5278 | 2014-12-14 | 1669131439 | |
| added row = new _timestamp => | 5 | Andy | AB-CF-48 | 7081 | 2003-07-05 | 1669221680 |
| added row = new _timestamp => | 6 | Beth | HH-FR-14 | 7541 | 2002-04-01 | 1669221680 |
- Incremental import A2 at Wed Nov 23 2022 16:42:42 GMT+0000 (1669221762)
| ID | NAME | SKU | VALUE | DATE | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| existing row, no new values => | 5 | Andy | AB-CF-48 | 7081 | 2003-07-05 |
| new row => | 7 | Edith | ED-BT-13 | 9471 | 1996-12-18 |
- Result of incremental import A2
Here we can see a significant change in the incremental load. The _timestamp column is updated for row id:5. For tables without native types, the row would not have the new value of _timestamp.
| ID | NAME | SKU | VALUE | DATE | _timestamp | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | John | CD-CZ-01 | 9247 | 2005-12-11 | 1669131439 | |
| 2 | Jack | CE-CA-22 | 3544 | 2012-10-14 | 1669131439 | |
| 3 | Jim | ED-BT-13 | 5262 | 2001-04-20 | 1669131439 | |
| 4 | Jil | BA-AB-11 | 5278 | 2014-12-14 | 1669131439 | |
| updating row = new _timestamp => | 5 | Andy | AB-CF-48 | 7081 | 2003-07-05 | 1669221762 |
| 6 | Beth | HH-FR-14 | 7541 | 2002-04-01 | 1669221680 | |
| added row = new _timestamp => | 7 | Edith | ED-BT-13 | 9471 | 1996-12-18 | 1669221762 |
- Import A3 at Wed Nov 23 2022 16:44:34 GMT+0000 (1669221874)
| ID | NAME | SKU | VALUE | DATE | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| existing row, with new value => | 5 | Andy | AB-CF-48 | 6081 | 2003-07-05 |
| existing row, no new values => | 7 | Edith | ED-BT-13 | 9471 | 1996-12-18 |
| new row => | 8 | Kate | CD-CZ-01 | 5282 | 2008-06-07 |
| new row => | 9 | Josh | BA-AB-11 | 6624 | 2004-10-04 |
| new row => | 10 | Arthur | EE-FF-66 | 596 2021-04-06 |
-
Result of incremental import A3
-
Here we can see another change that occurs only for tables with native types. The
_timestampcolumn for rowid:7is updated but there was no change in it.
| ID | NAME | SKU | VALUE | DATE | _timestamp | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | John | CD-CZ-01 | 9247 | 2005-12-11 | 1669131439 | |
| 2 | Jack | CE-CA-22 | 3544 | 2012-10-14 | 1669131439 | |
| 3 | Jim | ED-BT-13 | 5262 | 2001-04-20 | 1669131439 | |
| 4 | Jil | BA-AB-11 | 5278 | 2014-12-14 | 1669131439 | |
| updating row = new _timestamp => | 5 | Andy | AB-CF-48 | 6081 | 2003-07-05 | 1669221874 |
| 6 | Beth | HH-FR-14 | 7541 | 2002-04-01 | 1669221680 | |
| updating row = new _timestamp => | 7 | Edith | ED-BT-13 | 9471 | 1996-12-18 | 1669221874 |
| added row = new _timestamp => | 8 | Kate | CD-CZ-01 | 5282 | 2008-06-07 | 1669221874 |
| added row = new _timestamp => | 9 | Josh | BA-AB-11 | 6624 | 2004-10-04 | 1669221874 |
| added row = new _timestamp => | 10 | Arthur | EE-FF-66 | 596 | 2021-04-06 | 1669221874 |
Incremental Processing
When a table is loaded incrementally, the update time of each row is recorded internally. This information can be later used in input mapping of many components (especially transformations). Incremental processing is available in two flavors — automatic and manual. Incremental processing makes sense only for components reading data from the Storage (e.g., transformations and writers). Note that this is not supported for all components yet.
Automatic incremental processing
With automatic incremental processing, the component will receive only data modified from the last successful run of that component.
Extending the above example — if you have a table with a primary key defined on the column name:
| name | money |
|---|---|
| John | $150 |
| Peter | $340 |
| Darla | $600 |
and you import the following data to the table:
| name | money |
|---|---|
| Darla | $600000 |
| Peter | $340 |
| Annie | $500000 |
| Melanie | $900000 |
the result table will contain:
| name | money |
|---|---|
| John | $150 |
| Darla | $600000 |
| Peter | $340 |
| Annie | $500000 |
| Melanie | $900000 |
Notice that the record for Peter was not updated because it was not changed at all (the imported row was completely identical to the existing one). Therefore, when using incremental processing, that row will not be loaded in input mapping.
The component (e.g., writer) will receive only the highlighted rows. If there are no added or updated rows since the last successful run, an empty table will be passed to the component. The image below shows the setting of automatic incremental processing for the Snowflake writer:
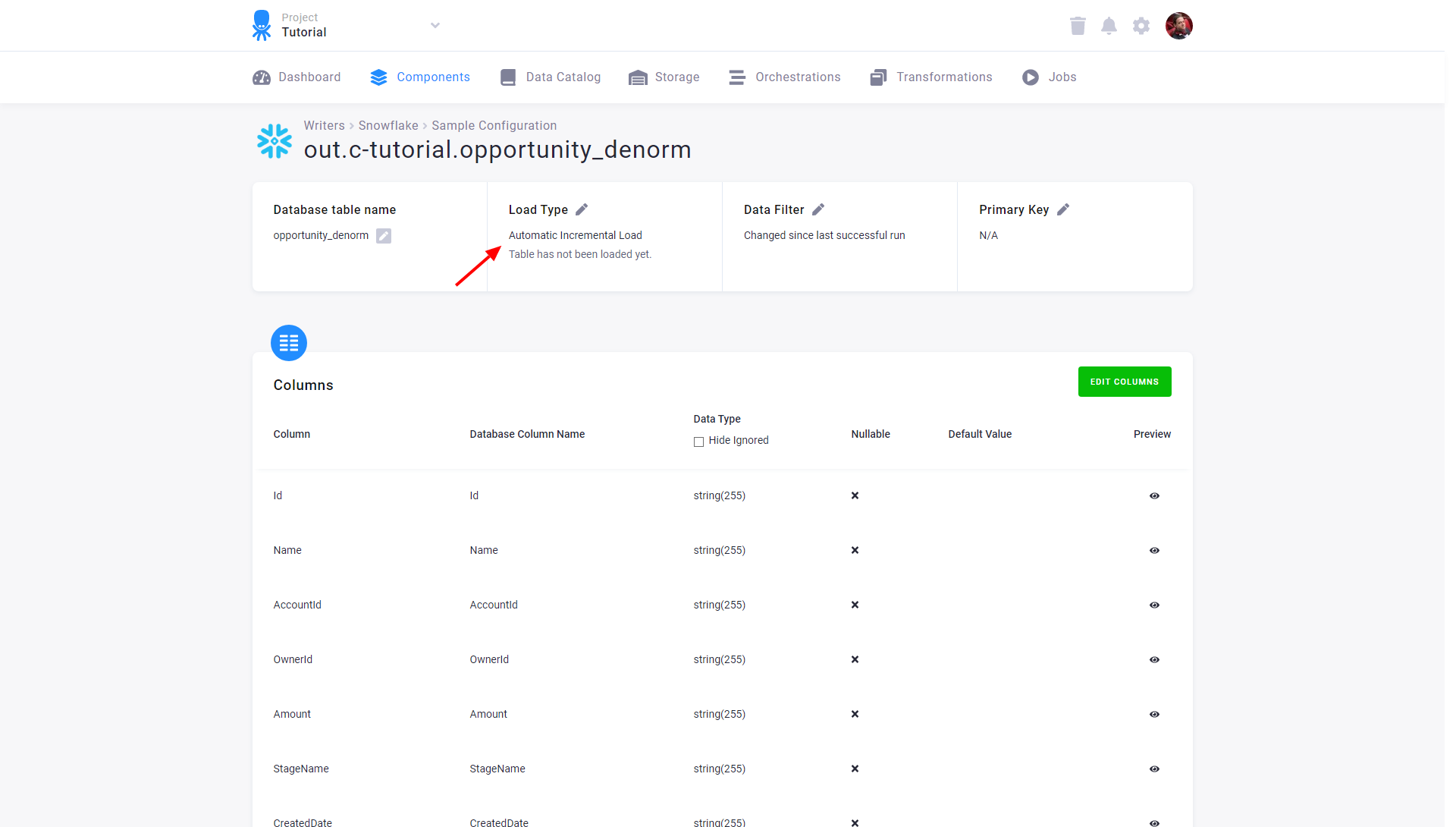
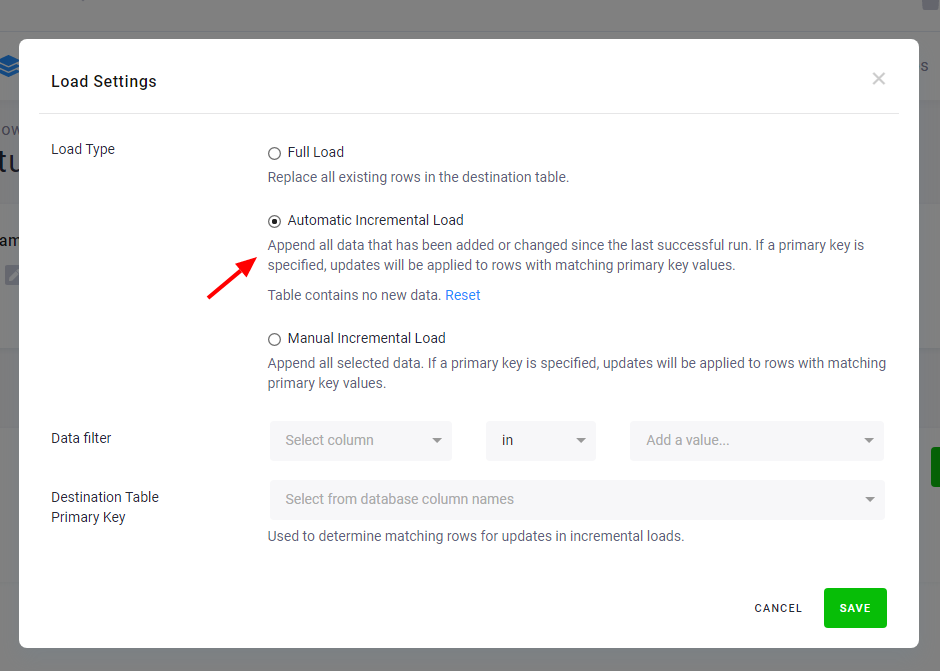
Automatic incremental processing offers the most efficient way to process data, but it is less transparent compared to processing the full tables. The date used to identify newly arrived data is stored internally and can be reset via the Reset button. This will cause the component to process the entire input table on the next run.
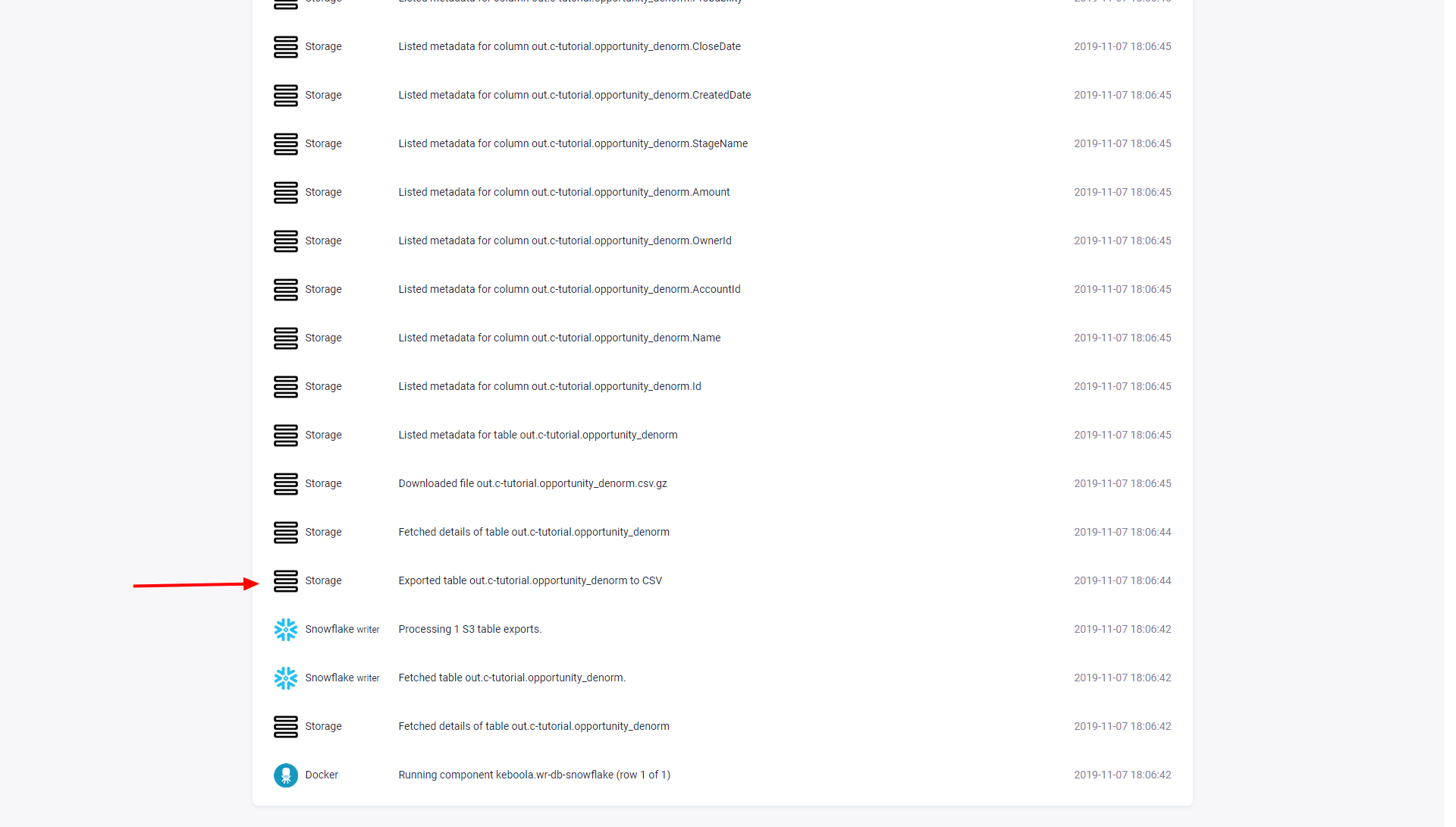
You can always verify the load date used in a particular job using the Job events. Search for an event Exported table X:
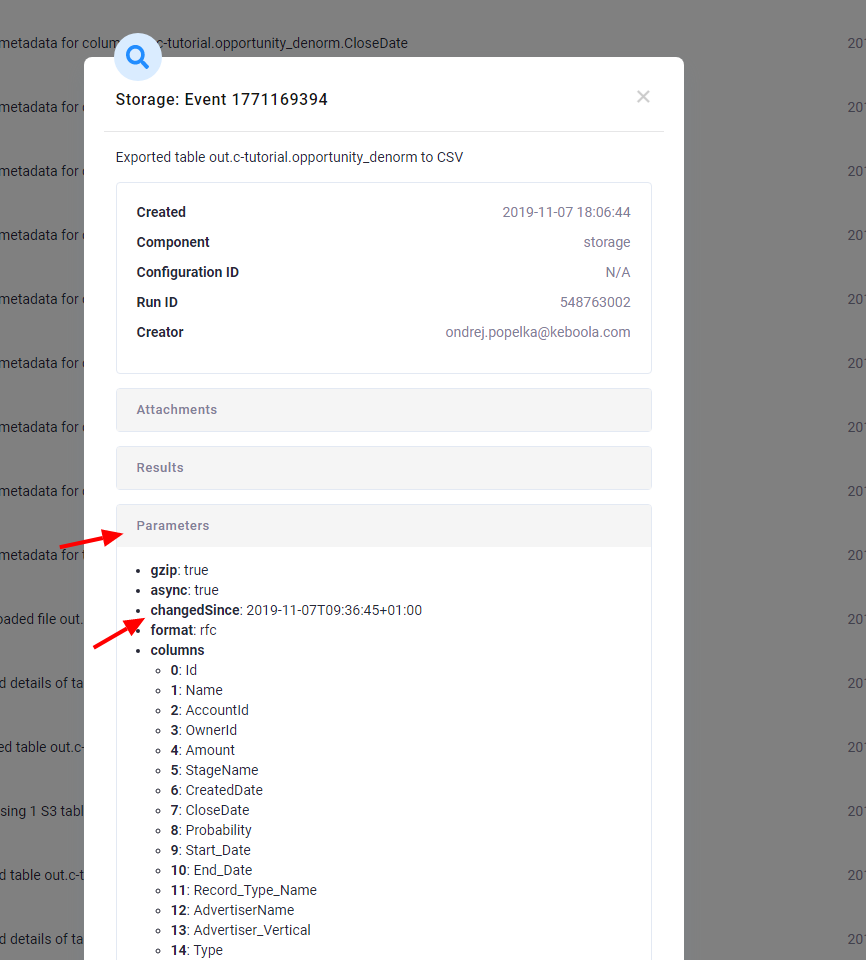
Click the event to show its detail; the changedSince parameter shows the date used to select the added and updated data:
Manual incremental processing
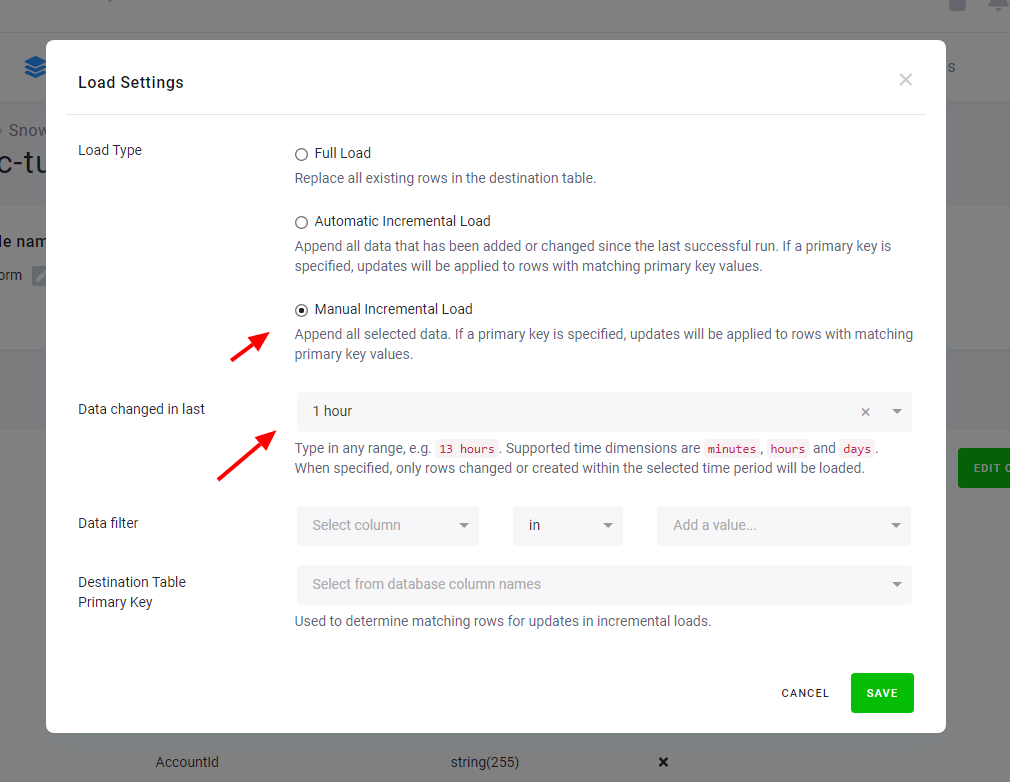
When the Automatic Incremental Processing feature is not available, or you
need greater control of the processing, you may specify the Changed in last option.
This enables the component to process only a specified increment of the data:
Extending the above example — if you have a table with a primary key defined on the column name:
| name | money |
|---|---|
| John | $150 |
| Peter | $340 |
| Darla | $600 |
and you import the following data to the table:
| name | money |
|---|---|
| Darla | $600000 |
| Peter | $340 |
| Annie | $500000 |
| Melanie | $900000 |
assuming that the import was on 2010-01-02 10:00, the result table will contain (the *_timestamp* column is not an actual column of the table, it is just displayed here for illustration purposes):
| name | money | *_timestamp* |
|---|---|---|
| John | $150 | 2010-01-01 10:00 |
| Darla | $600000 | 2010-01-02 10:00 |
| Peter | $340 | 2010-01-01 10:00 |
| Annie | $500000 | 2010-01-02 10:00 |
| Melanie | $900000 | 2010-01-02 10:00 |
Therefore, three rows in the table will be considered as changed (either added or updated). Now when you run a component (e.g., transformation)
with the Changed in last option, various things can happen:
Changed in lastis set to1 day, and the component is started any time between2010-01-02 10:00and2010-01-03 10:00– three rows will be exported from the table.Changed in lastis set to1 day, and the component is started any time after2010-01-03 10:00– no rows will be exported from the table.Changed in lastis set to2 day, and the component is started any time between2010-01-02 10:00and2010-01-03 10:00– five rows will be exported from the table.
Notice that the record for Peter was not updated because it did not change (the
imported row was completely identical to the existing one). Therefore,
when using incremental processing set to 1 day, that row will not be included in the input mapping.
Truncate Table
Overview
The Truncate Table feature removes all records from a table while preserving its schema (column structure and metadata). The feature deletes all rows but keeps the table structure intact. Primary keys or metadata remain without change. The feature is highly efficient especially when replacing an entire dataset.
When to Use Truncate Table?
- Replacing data completely (e.g., daily refresh of customer records).
- Ensuring clean data ingestion without duplication.
- Automating scheduled table resets (e.g., overwriting temporary datasets).
How to Truncate a Table:
- Navigate to Storage → Tables.
- Select the table you want to truncate.
- Click the three dots on the right side of the screen. A drop-down menu will display.
- Select “Truncate table”. A warning information will display.
- Confirm clicking the “Truncate table” button.
Delete Rows
Overview
The Delete Rows feature allows you to remove specific records from a table in Storage. Unlike Truncate Table, which clears all data, Delete Rows selectively removes only matching records, keeping the rest of the table intact.
When using the Delete Rows feature, you can apply multiple filters in a single execution, such as:
- Rows changed within a specific period.
- Rows containing a specific value in a given column. Before deleting the rows, Keboola displays a preview of the records that will be removed based on your filters.
When to Use Delete Rows?
- Removing outdated records (e.g., inactive customers).
- Correcting erroneous data entries.
- Synchronizing data with external systems (e.g., deleting stale records).
How to Delete Rows:
- Navigate to Storage → Tables.
- Select the table where you want to delete rows.
- Click the three dots on the right side of the screen to open a drop-down menu.
- Select “Delete Rows”. A pop-up will appear.
- Set up the filters to specify which rows should be deleted.
- Click “Delete rows” to confirm.
