GoodData
This data destination connector sends tables into a GoodData project.
Before configuring the GoodData connector, it is important to understand that GoodData relies on a Logical Data Model (LDM) of your dataset. The GoodData data destination connector creates the LDM for you so that you don’t have to use CloudConnect or other tools provided by GoodData. However, you need to provide all the required information in the configuration. This makes the configuration non-trivial, and you should have the data model designed before you start configuring the connector.
Configuration
Create a new configuration of the GoodData connector.
The first step is to configure the GoodData project that will be used for writing:
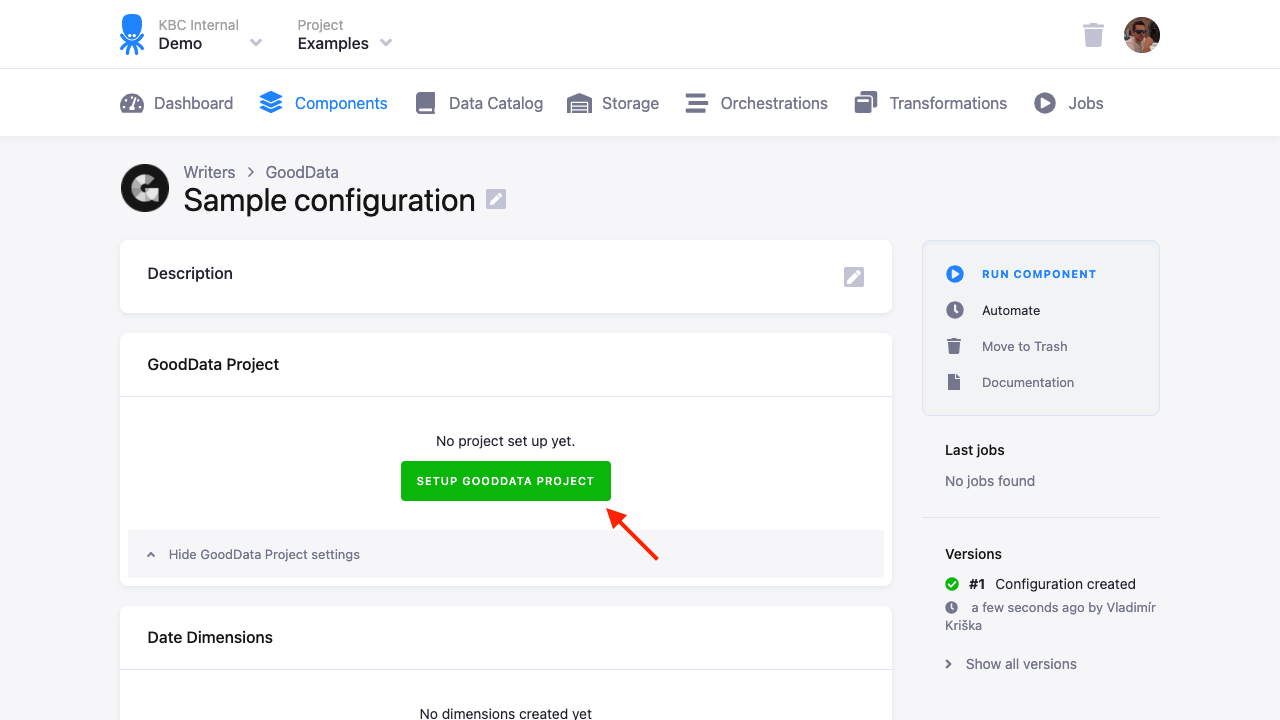
Project Setup
There are several options in the configuration dialog:
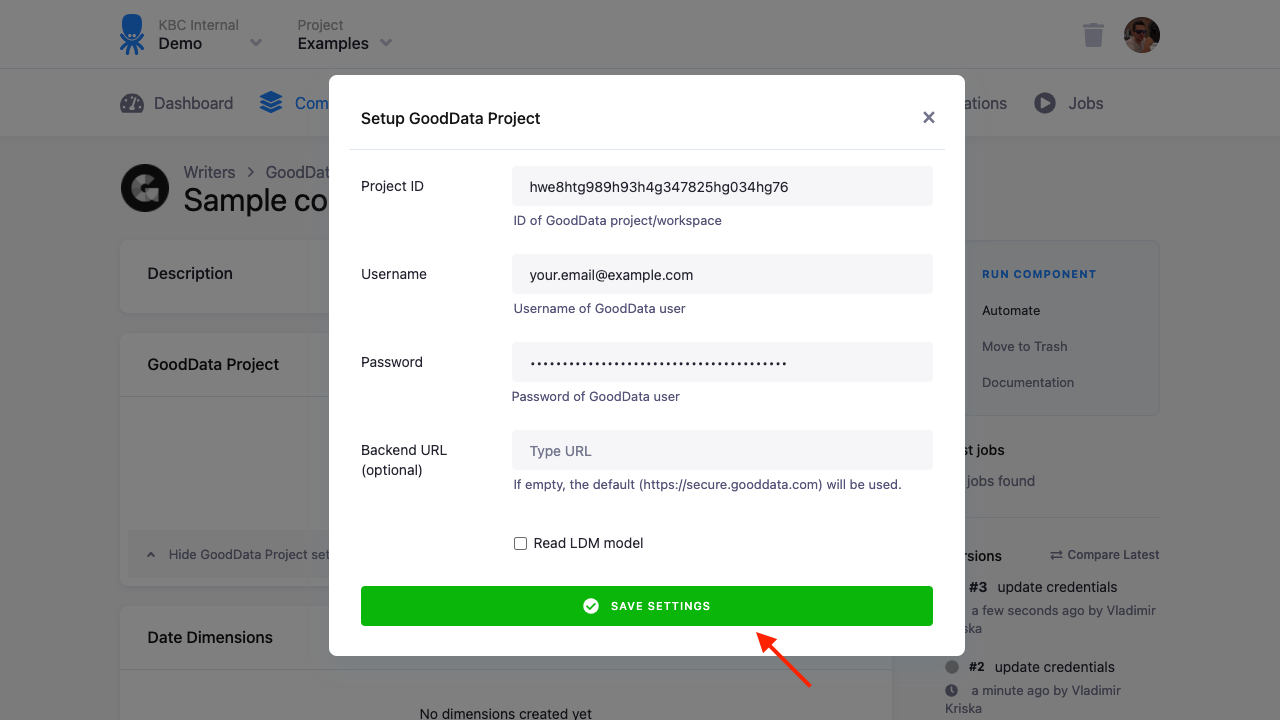
When using an existing GoodData project, the project should be empty, or you should take extra care when setting up the data destination connector. Either use Load data only update mode, or be sure to understand what the consequences of changing your LDM are.
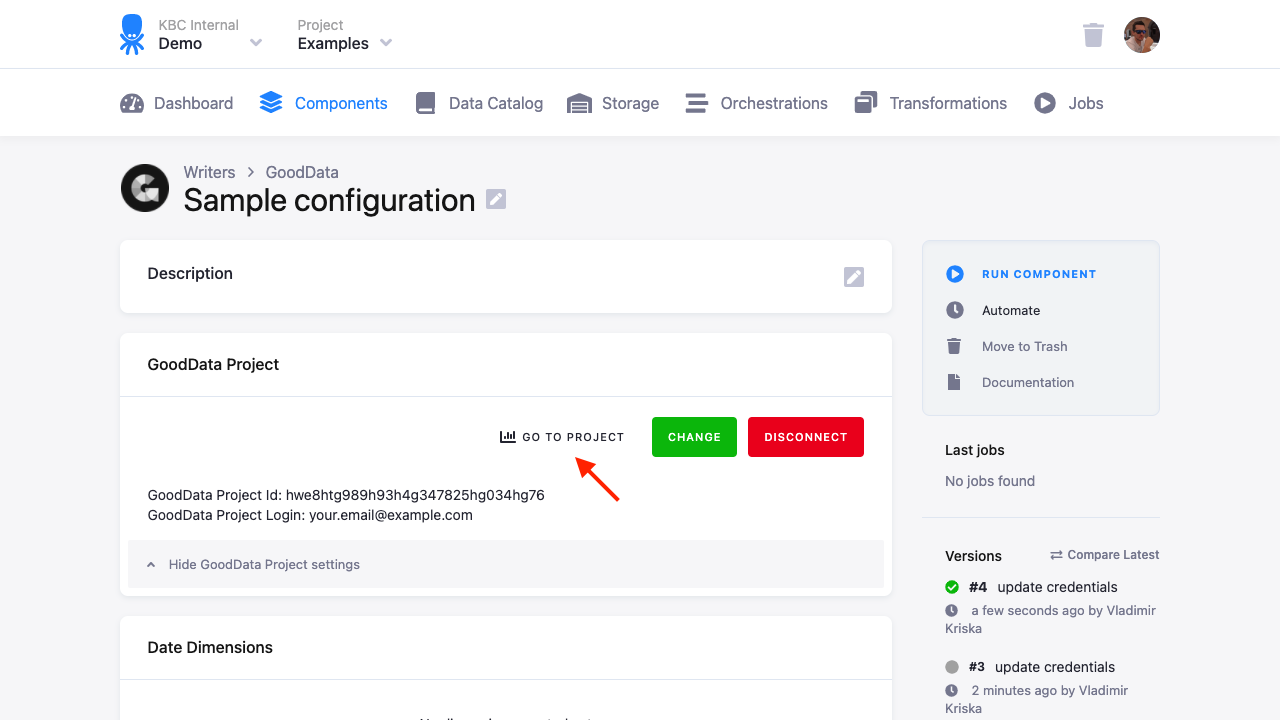
After you set up the project, you will see the Go To Project button.
Date Dimension
Date dimension is an important concept of the GoodData LDM. It is the question of the LDM design to determine for which columns a date dimension should be created. One rule of thumb is that different date columns in a single table should have different date dimensions. On the other hand, you might want to share a date dimension between different tables — a main date representing an event of something. It is also possible to have different date dimensions representing, e.g., a calendar year and a fiscal year.
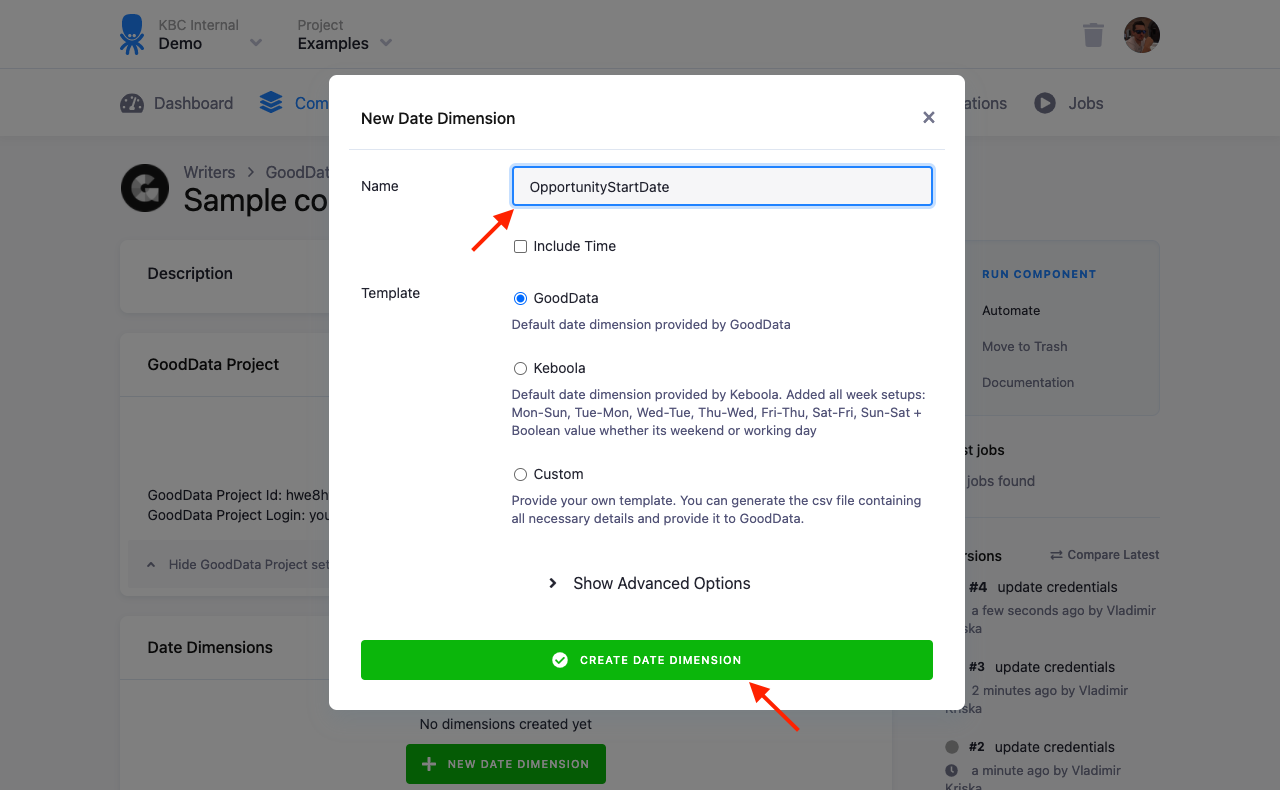
When creating a date dimension, you have to enter the dimension name and a dimension template. The available templates are:
- Standard GoodData date dimension
- Keboola date dimension, which is extended with a ‘floating’ week (it lets you analyze data as if the week starts, e.g., on Wednesday).
- Custom date dimension – this can be either a date dimension created for you directly by GoodData, or a Self service calendar. In the former case, you will have the dimension URN in the form
urn:my-company-dimension:date, entermy-company-dimensionas Template ID. For the latter case, entercustomas the Template ID.
Configure Tables
Click the New Table button to add a new table to the connector:
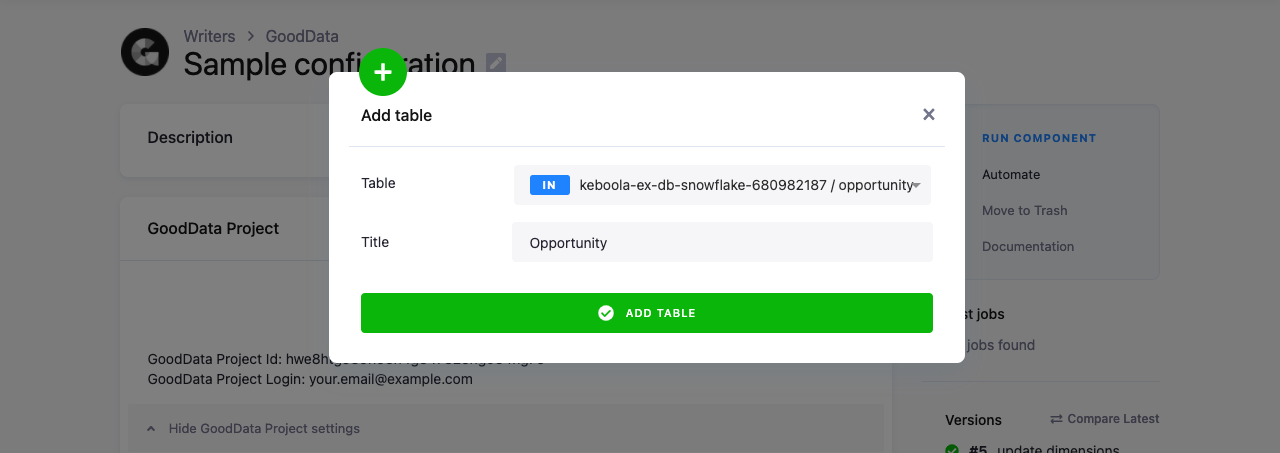
Select an existing table from the storage and enter a Title which will be used for the table in the GoodData project (you can change the title later if needed). The next step is to configure the table columns.
- Important: There is a hard limit on the GoodData interface (Workspace loading limit; link requires authentication) which allows to load only 25 GB of CSV data in a single load of a single table. If you are nearing this limit, we suggest you split the table into chunks and load it incrementally. Feel free to contact our support for more help.*
Table Columns
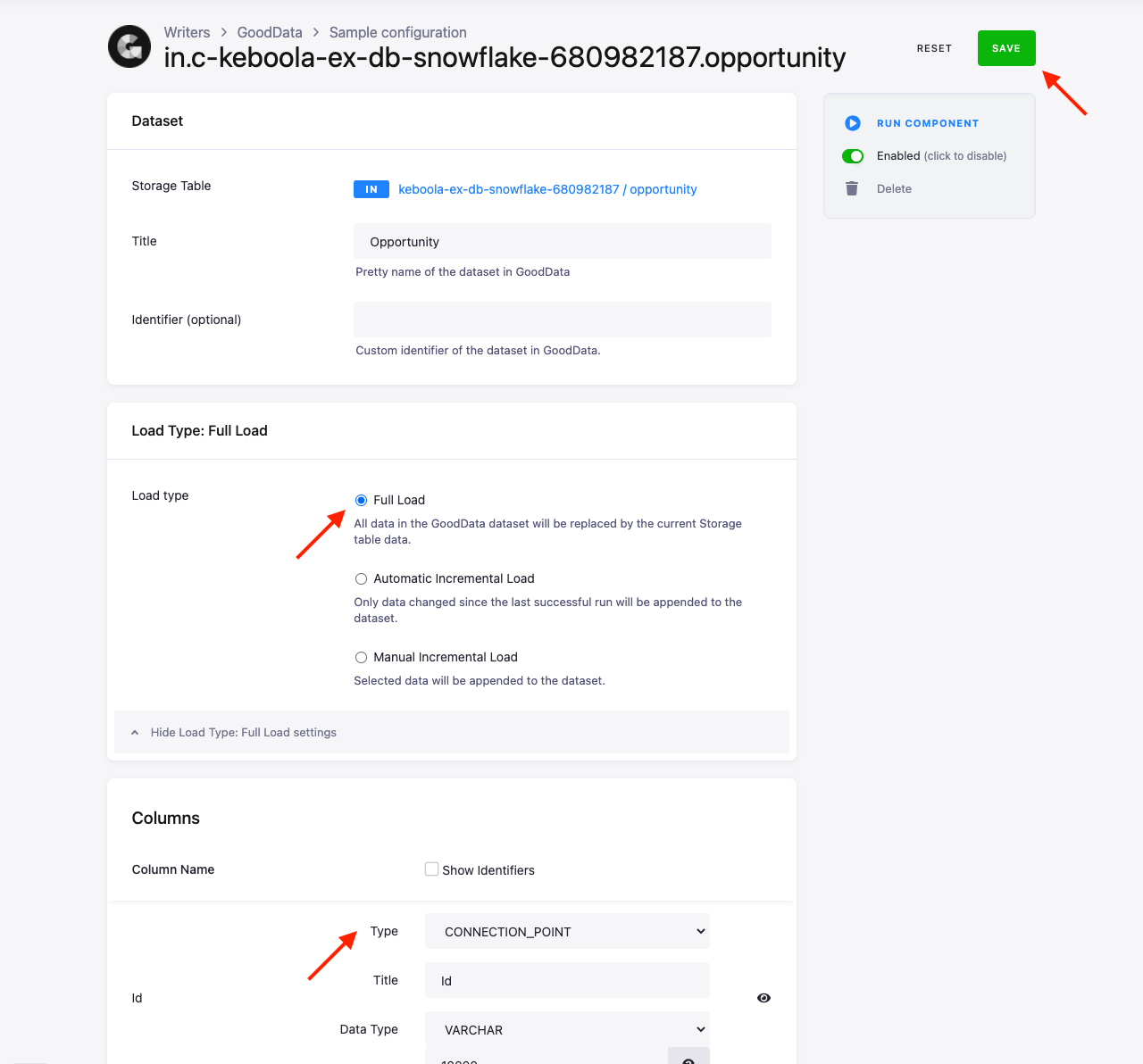
Setting the table columns involves configuration of three things:
- Title of the column that is displayed in the GoodData project
- Data Type of the column. You can choose from
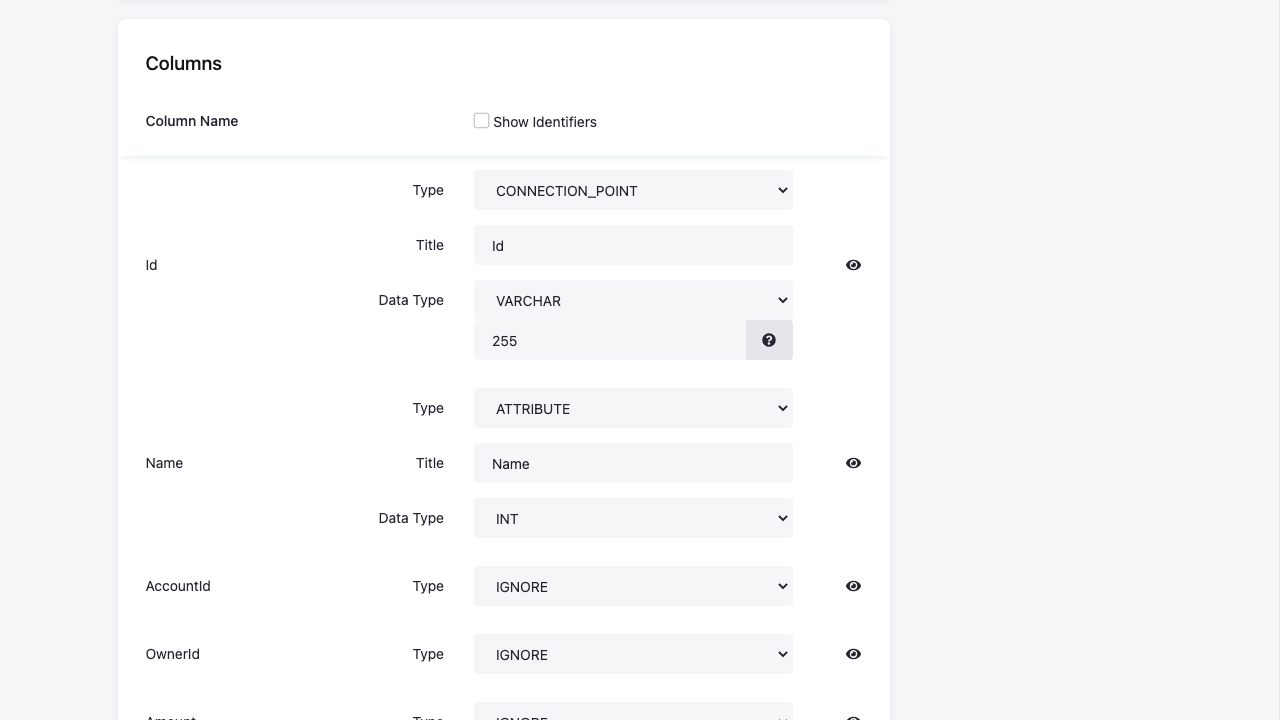
INT,BIGINT,DECIMALfor numbers,VARCHARfor texts. Consult the GoodData documentation for the limits of each data type. - Type of the column that defines the role of the column in LDM. The column types are:
IGNORE— The column is excluded from the load and will not be created in the GoodData project.FACT— The Fact component — a numerical piece of arbitrary data used to define metrics, e.g., Price column.ATTRIBUTE— The Attribute component of the LDM model — a discrete set of alphanumeric or numeric data, e.g., Eye Color column containing values Blue, Brown, and Green.CONNECTION_POINT— The Connection point component — acts like a primary key, i.e., it is used to identify the rows of the table.REFERENCE— A column which defines a Relation between tables. You have to select a Reference column as a target to which the relation points to. The target must be aCONNECTION_POINTalready defined in another table.DATE— A date column — you have to select a corresponding date dimension for it.LABEL— A Label attribute that allows you to display alternative values for a column. You have to select a Reference column, which is the name of an attribute column in the same table. The label column is used as a secondary view of the reference column in the GoodData UI. For example, you can create a reference columnFullNameand add a label columnSurname. You can define multiple labels for a single attribute.HYPERLINK— A Hyperlink attribute, which acts as a link in the reports. You have to select a Reference, which is the name of an attribute column in the same table. The reference column is the one that will be used as a label, the hyperlink column is the one that is expected to contain the address.
Save your configuration.
Additional Table Options
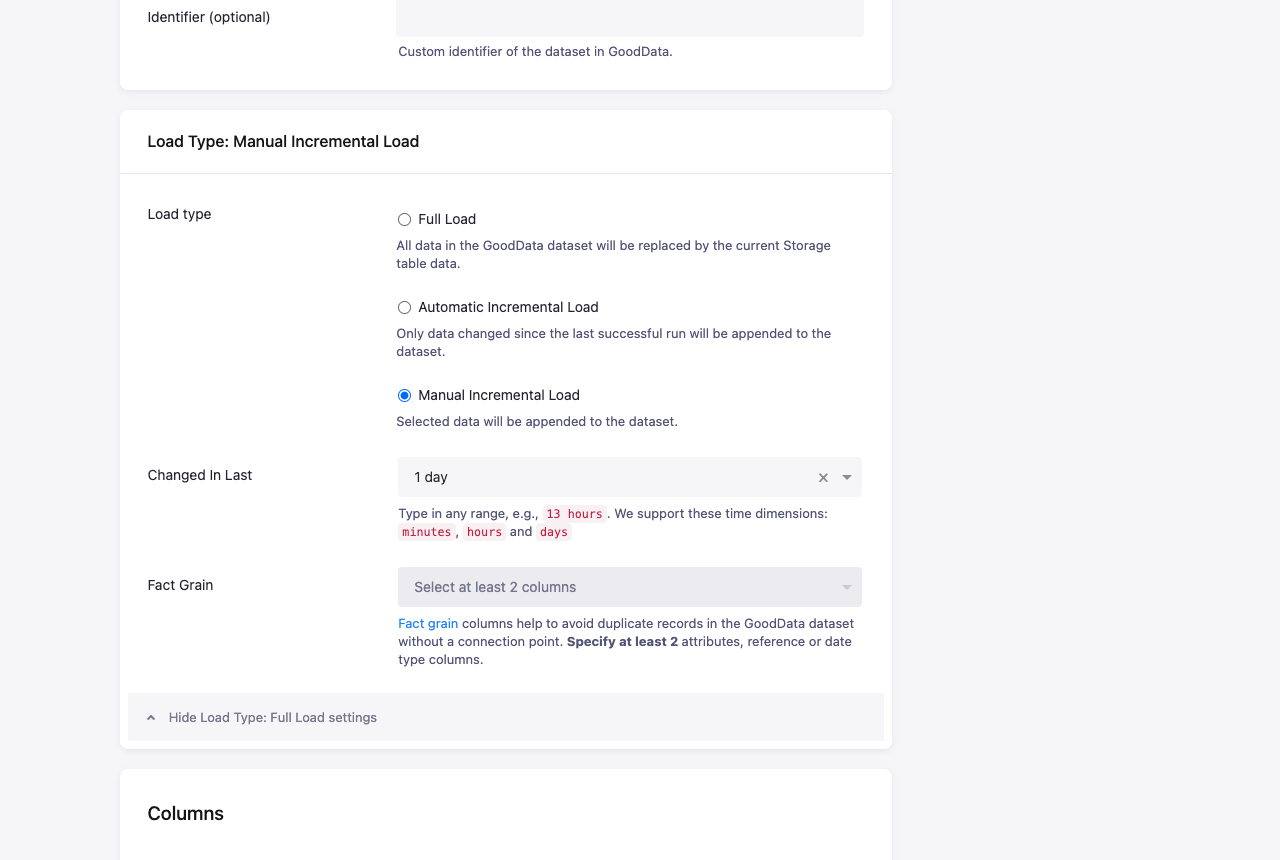
You can also select a load type: Full Load (the default), Automatic Incremental Load or Manual Incremental Load. Incremental load will keep the existing data in the GoodData project. It can be much faster, but the source data needs to be correctly prepared. The incremental load relies on the following two features:
- Incremental processing in Storage, and
- Identity in GoodData; this can be either a
CONNECTION_POINTcolumn (which acts as a database primary key), or a Fact Grain (which acts as a compound unique key). Fact Grain can be used when there is no single identifying column (i.e. there is noCONNECTION_POINT) and there is a combination of columns which can be used to identify rows. If there is no such combination, then incremental loading cannot be used.
From the table configuration page, you can also Run a load of a single table. However, if the table has relations to other
tables, it will fail with the message: Schema reference of column 'X' of dataset Y is invalid.
Writing Data
There are multiple options how you can write data to a GoodData project:
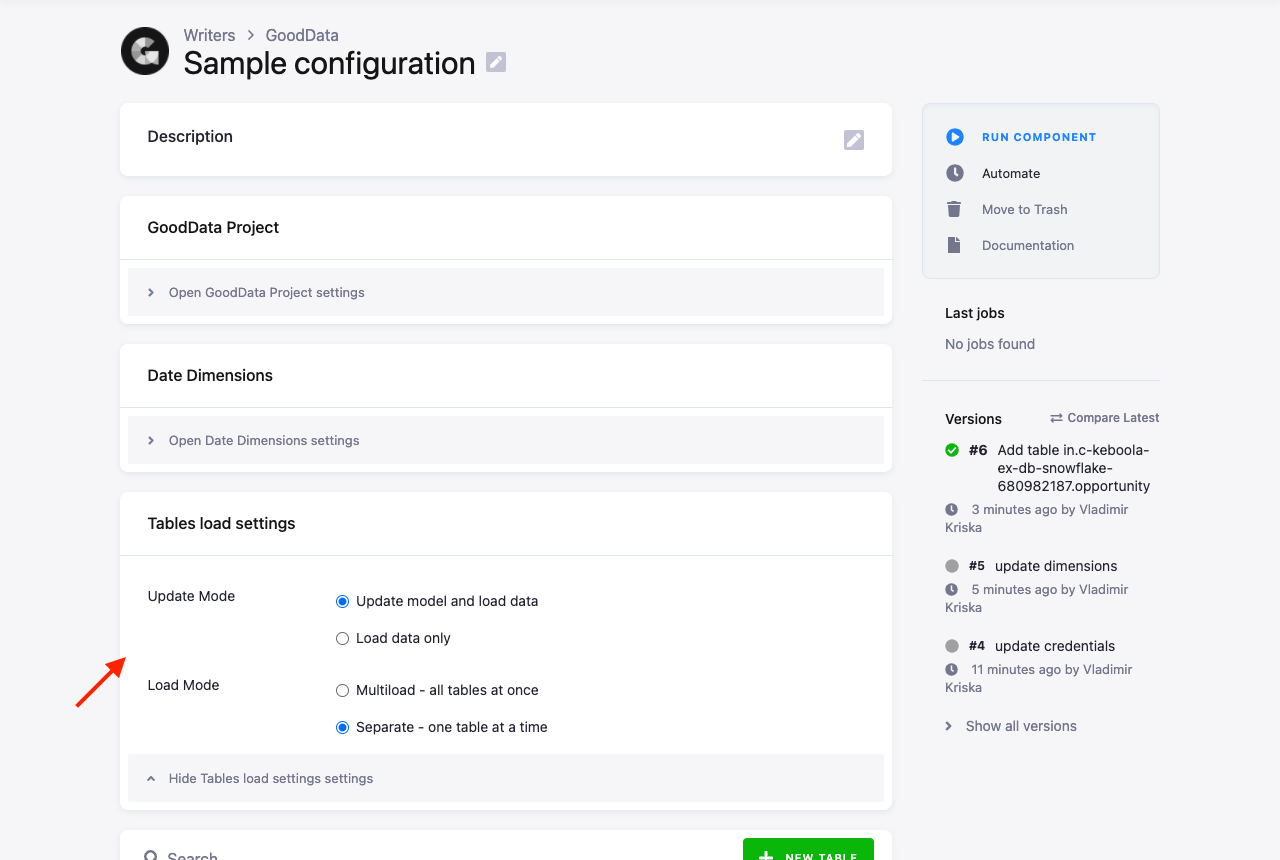
By default, the LDM is updated with each run of the data destination connector. If your project structure settled down and does not
change often, you may wish to switch to Load data only mode. This saves some time from each run and also
is somewhat safer against inadvertent changes of the model. When you change the LDM definition in the connector and load data
without updating the model, you are likely to receive an error similar to this: "The object identifier "XY" mentioned in the manifest
does not represent a valid object. Adjust the manifest or create the object.".
Another option is to switch between Separate load and Multiload. These represent different modes of transferring data into GoodData, and depending on the size and nature of your project, either of them may be faster.
GoodData Project
Since the project is partially managed by the data destination connector, there are some things you should be aware of.
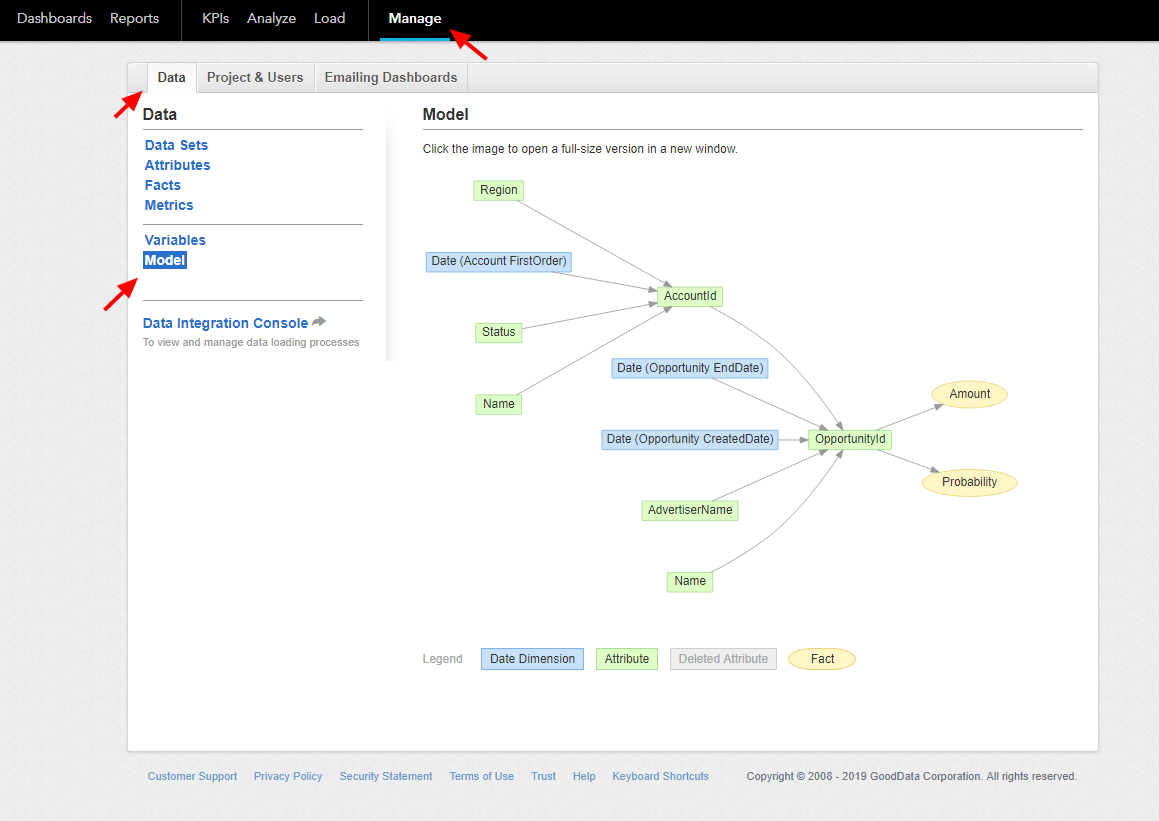
The connector manages the LDM in the project. If you make changes to the LDM using other tools, they will be overwritten by the connector — unless it is used solely in Load data only mode. You can review the LDM in the GoodData project management: